Natural Language Processing (NLP)
1. What is NLP ?

Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It combines linguistics, machine learning, and deep learning to process text and speech, allowing machines to interact with humans naturally. NLP is used in various applications, including chatbots, virtual assistants, machine translation, sentiment analysis, and speech recognition.
NLP techniques include Tokenization, Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging, Named Entity Recognition (NER), Sentiment Analysis, and Text Summarization. Tokenization breaks text into words or sentences, while POS Tagging identifies grammatical roles like nouns and verbs. NER extracts names, dates, and locations, and Sentiment Analysis determines emotions in text. Text Summarization condenses large text into shorter, meaningful summaries.
Popular NLP models include BERT, GPT, and Transformer-based architectures, which enhance machine comprehension of natural language. Real-world applications of NLP include Google Search, Siri, Alexa, spam filters, and customer support automation. As AI advances, NLP continues to improve human-computer interactions, making technology more intelligent and user-friendly.
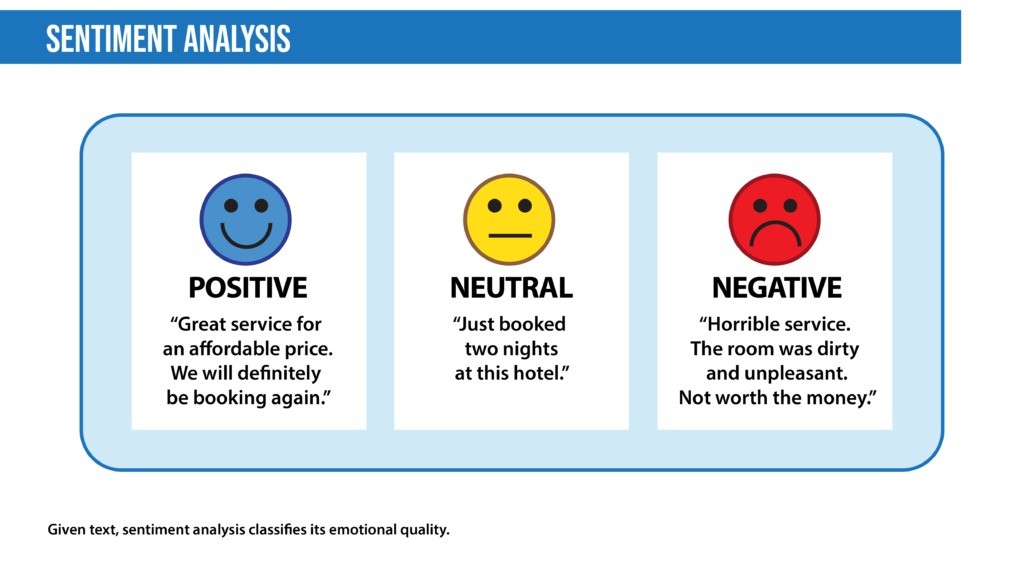
2. Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment Analysis, also known as opinion mining, is a Natural Language Processing (NLP) technique used to determine the emotional tone behind a piece of text. It helps classify text as positive, negative, or neutral, making it useful for analyzing opinions, customer feedback, and social media sentiments.
Sentiment Analysis uses machine learning models, lexicon-based approaches, and deep learning techniques to interpret emotions in text. Machine learning models, such as Naïve Bayes, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Deep Learning models like BERT, are commonly used. Lexicon-based approaches rely on predefined word lists with assigned sentiment scores.
Real-world applications of Sentiment Analysis include customer feedback analysis, brand reputation monitoring, political sentiment tracking, and product reviews analysis. Businesses use it to understand customer emotions, improve products, and enhance marketing strategies. Despite its effectiveness, challenges like sarcasm detection, context understanding, and multilingual processing remain, requiring continuous advancements in NLP techniques.
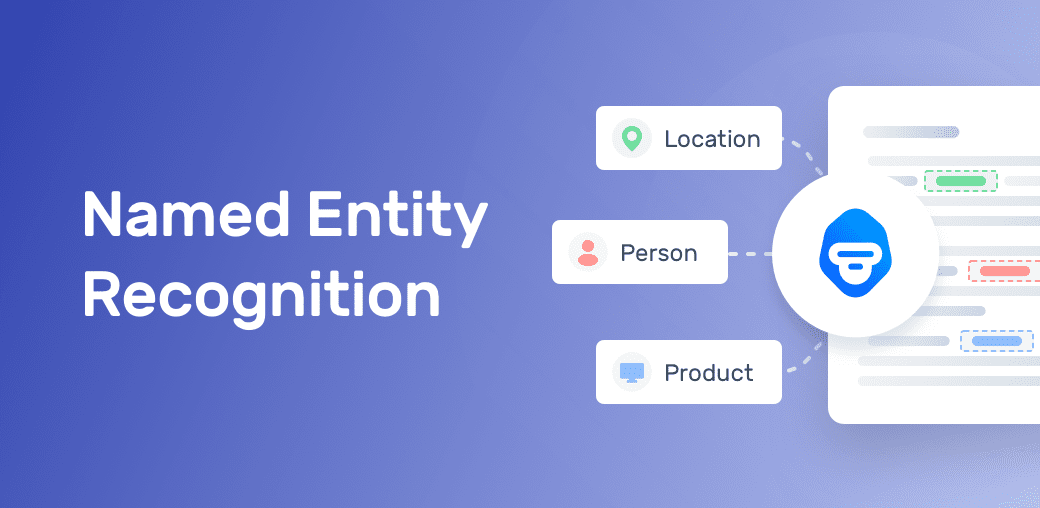
3. Named Entity Recognition
Named Entity Recognition (NER) is a key technique in Natural Language Processing (NLP) that identifies and classifies specific entities in text into predefined categories such as names of people, organizations, locations, dates, quantities, and more. It helps extract structured information from unstructured text, making it useful for search engines, chatbots, and data analysis.
NER typically works in two steps:
1. Identifying Named Entities – The model detects words or phrases that represent an entity.
2. Classifying Entities – The recognized words are categorized into groups like PERSON (e.g., "Elon Musk"), ORGANIZATION (e.g., "Google"), LOCATION (e.g., "New York"), DATE (e.g., "January 1, 2025"), etc.
NER is widely used in news aggregation, financial analysis, legal document processing, and healthcare to extract key details from large text datasets. Popular NLP models like BERT, spaCy, and NLTK use deep learning to improve NER accuracy. However, challenges like context ambiguity, variations in entity names, and multilingual processing make it a complex task, requiring continuous improvements in NLP models.
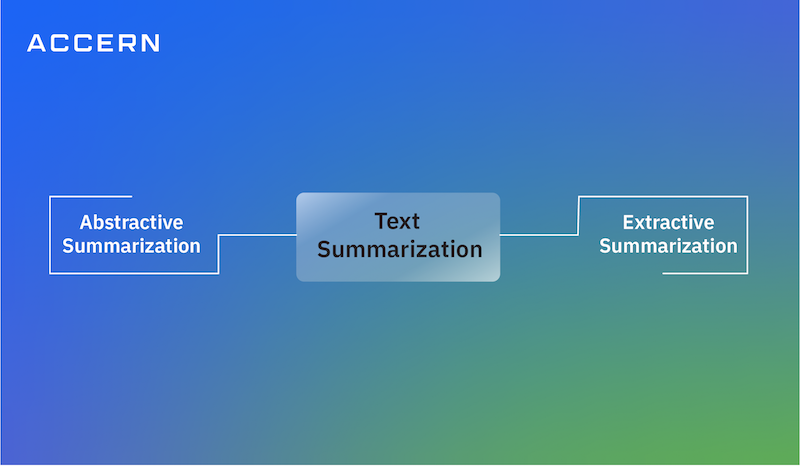
4. Text Summarization
Text Summarization is a Natural Language Processing (NLP) technique that automatically generates a short, meaningful summary of a larger text while preserving key information. It helps process large amounts of data efficiently, making it useful for news summarization, research papers, legal documents, and customer reviews.
There are two main types of Text Summarization:
1. Extractive Summarization – Selects the most important sentences or phrases directly from the original text without modifying them. Example: TextRank, LexRank algorithms.
2. Abstractive Summarization – Generates a summary by understanding the meaning of the text and rewriting it in a concise way. Example: Transformer models like BERT, GPT, and T5.
Text Summarization is widely used in search engines, chatbots, content recommendations, and academic research. It improves readability and saves time by condensing lengthy documents into key insights. However, challenges like maintaining context, handling complex language, and avoiding loss of critical information make it an evolving field in NLP
5. Speech-to-Text (STT)
Speech-to-Text (STT), also known as Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), is a Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology that converts spoken language into written text. It is widely used in voice assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa), transcription services, customer support, and accessibility tools for people with disabilities.
STT systems use machine learning, deep learning, and linguistic models to process and transcribe audio. The process involves:
Audio Processing – Converting speech into a digital waveform.
Feature Extraction – Identifying key sound patterns like phonemes.
Model Recognition – Using Neural Networks (e.g., DeepSpeech, Whisper, Wav2Vec) to convert sounds into text.
Modern STT models leverage AI-powered techniques like Transformer models and deep learning for higher accuracy, even in noisy environments. However, challenges such as background noise, accents, multiple speakers, and language variations require ongoing advancements in speech recognition technology
6. Text-to-Speech (TTS)
Text-to-Speech (TTS) is a Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology that converts written text into spoken audio. It is widely used in voice assistants (Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant), audiobooks, accessibility tools for visually impaired users, and customer service chatbots. TTS systems use machine learning, deep learning, and speech synthesis techniques to generate human-like speech. The process involves text preprocessing, where the system analyzes grammar, punctuation, and pronunciation, followed by speech synthesis, where AI models generate sound waves that mimic human speech. Modern TTS models, such as Google WaveNet, Tacotron, and Amazon Polly, use deep learning and neural networks to produce more natural and expressive voices. However, challenges like intonation, emotional expression, and handling multilingual text still require continuous improvements. TTS technology is evolving rapidly, making interactions with digital systems more natural and accessible.
Text-to-Speech (TTS) technology plays a crucial role in enhancing human-computer interaction by enabling machines to communicate using natural-sounding speech. Traditional TTS systems relied on concatenative synthesis, where pre-recorded speech segments were joined together, but modern advancements use deep learning-based synthesis like WaveNet, Tacotron, and FastSpeech, which generate more fluid and expressive voices. These models analyze intonation, stress, and rhythm to create speech that closely resembles human conversation. TTS is extensively used in smart devices, virtual assistants, navigation systems, and educational applications, making information more accessible to users.
With advancements in AI and deep learning, TTS is now capable of expressing emotions, adjusting speech styles, and supporting multiple languages and accents. This is particularly beneficial for language learning, accessibility tools for visually impaired users, and audiobook production. Additionally, voice cloning and personalized synthetic voices are emerging trends, allowing users to create custom AI voices that mimic real human speech. However, challenges like maintaining natural pronunciation, handling complex text structures, and preventing misuse for deepfake audio remain key concerns in the development of TTS technology.
7. Chatbots
Chatbots are AI-powered virtual assistants designed to simulate human conversations through text or voice interactions. They use Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to understand user queries and generate relevant responses. Chatbots are widely used in customer service, e-commerce, healthcare, education, and entertainment to provide instant support and automate repetitive tasks. They can be categorized into rule-based chatbots, which follow predefined scripts, and AI-driven chatbots, which learn from interactions and improve their responses over time. Advanced chatbots, like ChatGPT, Google Bard, and IBM Watson, leverage deep learning and large language models (LLMs) to handle complex queries with human-like responses.
Modern chatbots are evolving with context awareness, sentiment analysis, and multilingual capabilities, making them more interactive and efficient. They integrate with messaging platforms (WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Slack), websites, and mobile apps to enhance customer engagement. Businesses use chatbots for automated support, lead generation, personalized recommendations, and appointment scheduling. However, challenges such as understanding sarcasm, handling ambiguous queries, and ensuring data privacy still require continuous improvements. As AI advances, chatbots will become even more intelligent, offering seamless human-computer interactions in various industries.
Chatbots have significantly transformed the way businesses and individuals interact with technology. With advancements in machine learning (ML) and deep learning, modern chatbots can adapt, learn from past interactions, and provide more accurate responses over time. AI-driven chatbots, such as ChatGPT and Google Bard, use large language models (LLMs) trained on vast amounts of data to understand and generate human-like text. This makes them capable of handling complex queries, maintaining context, and even recognizing emotions through sentiment analysis. Additionally, voice-enabled chatbots integrated with text-to-speech (TTS) and speech-to-text (STT) technologies allow for a more natural, hands-free user experience in smart assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
The future of chatbots lies in enhanced personalization, emotion detection, and improved contextual understanding. Businesses are increasingly using AI-powered chatbots to offer 24/7 customer support, automate HR tasks, assist in online shopping, and provide financial advice. In healthcare, chatbots are helping patients by scheduling appointments, offering mental health support, and answering medical queries. However, challenges such as ethical concerns, misinformation, data security, and bias in AI responses remain crucial aspects to address. With continuous advancements, chatbots are expected to become more human-like, emotionally intelligent, and seamlessly integrated into daily life, making human-computer interactions more natural and efficient
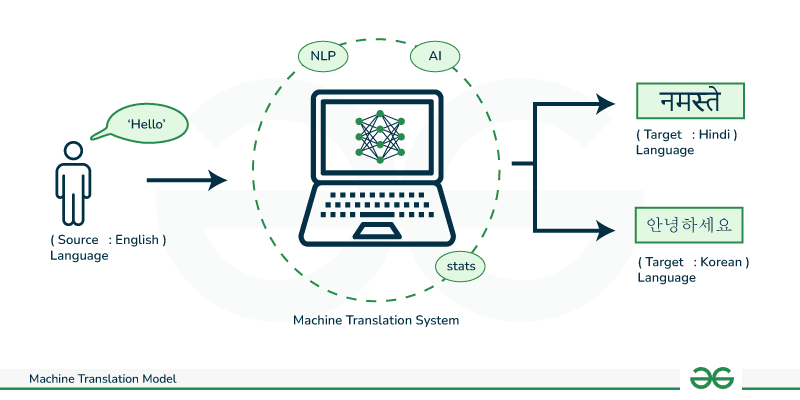
8. Machine Translation
Machine Translation (MT) is a subfield of Natural Language Processing (NLP) that enables computers to automatically translate text or speech from one language to another. It eliminates the need for human translators, making communication across different languages faster and more accessible. Traditional machine translation systems relied on rule-based or statistical methods, which used predefined grammatical rules or statistical models to translate text. However, modern MT has advanced significantly with the introduction of Neural Machine Translation (NMT), which leverages deep learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to produce more accurate and natural translations. Popular machine translation tools include Google Translate, DeepL, Microsoft Translator, and Amazon Translate.
NMT models use transformers and attention mechanisms to understand the context and meaning of words, improving translation quality. These models analyze entire sentences rather than translating word-by-word, resulting in more fluent and human-like translations. Machine translation is widely used in global businesses, travel, education, customer support, and content localization. However, challenges such as handling idioms, cultural nuances, grammar complexities, and low-resource languages still exist. As AI continues to evolve, future advancements in machine translation aim to improve accuracy, context awareness, and real-time conversational translation, breaking down language barriers and enhancing global communication.
Machine Translation (MT) is continuously evolving with the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and deep learning models. Modern systems, such as Google’s Transformer-based BERT and OpenAI’s GPT, have significantly improved translation quality by considering context, sentence structure, and even cultural nuances. Real-time translation tools, like Google Lens and Meta’s AI-powered speech translation, allow users to translate text from images, videos, and live conversations, making cross-language communication seamless. Moreover, businesses use custom-trained MT models to translate technical documents, legal texts, and medical research with domain-specific accuracy.
Despite these advancements, MT still faces challenges in understanding regional dialects, sarcasm, and ambiguous words. Languages with limited digital resources (low-resource languages) often suffer from lower translation accuracy. Additionally, AI bias and data privacy concerns raise ethical issues, as inaccurate translations can lead to misunderstandings in critical fields like healthcare, law, and diplomacy. Future developments in hybrid AI models, multimodal translation (text, audio, and video), and real-time AI interpreters will further enhance machine translation, making it more precise, context-aware, and universally accessible
Comments