Big Data & Analytics
Big Data refers to massive volumes of structured and unstructured data, while Analytics involves processing and analyzing this data to extract valuable insights for decision-making.
Big Data refers to massive volumes of structured and unstructured data, while Analytics involves processing and analyzing this data to extract valuable insights for decision-making.
Big Data refers to the massive volume of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data generated from various sources, such as social media, IoT devices, financial transactions, healthcare records, and e-commerce platforms. The fundamental characteristics of Big Data are described by the 3Vs: Volume (large amount of data), Velocity (fast data generation and processing), and Variety (different data formats, including text, images, videos, and sensor data). Some modern definitions also include Veracity (data accuracy and trustworthiness) and Value (usefulness of data insights). Traditional databases struggle to handle such vast amounts of data, which is why Big Data technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases are used for efficient processing and analysis.
The primary goal of Big Data is to extract meaningful insights and patterns that can help businesses and organizations make data-driven decisions. Data collection, storage, and analysis are crucial aspects of Big Data processing. Distributed computing frameworks, such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, enable parallel data processing across multiple nodes, allowing for scalability and faster computations. Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) play a crucial role in analyzing Big Data, helping to identify trends, detect anomalies, and automate decision-making processes. Cloud computing services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure provide powerful infrastructure for storing and processing Big Data at scale.
Big Data is revolutionizing industries by enabling predictive analytics, personalized recommendations, fraud detection, and operational efficiency. In healthcare, Big Data is used to analyze patient records, detect disease patterns, and improve treatment outcomes. In finance, it helps in fraud prevention and real-time risk assessment. In retail and e-commerce, companies leverage Big Data to offer personalized product recommendations and optimize supply chain management. However, data privacy, security, and ethical concerns remain challenges that organizations must address when dealing with vast amounts of sensitive user data. With continuous advancements in AI, cloud computing, and data science, Big Data will continue to drive innovation and transformation across industries.
Click here for more information

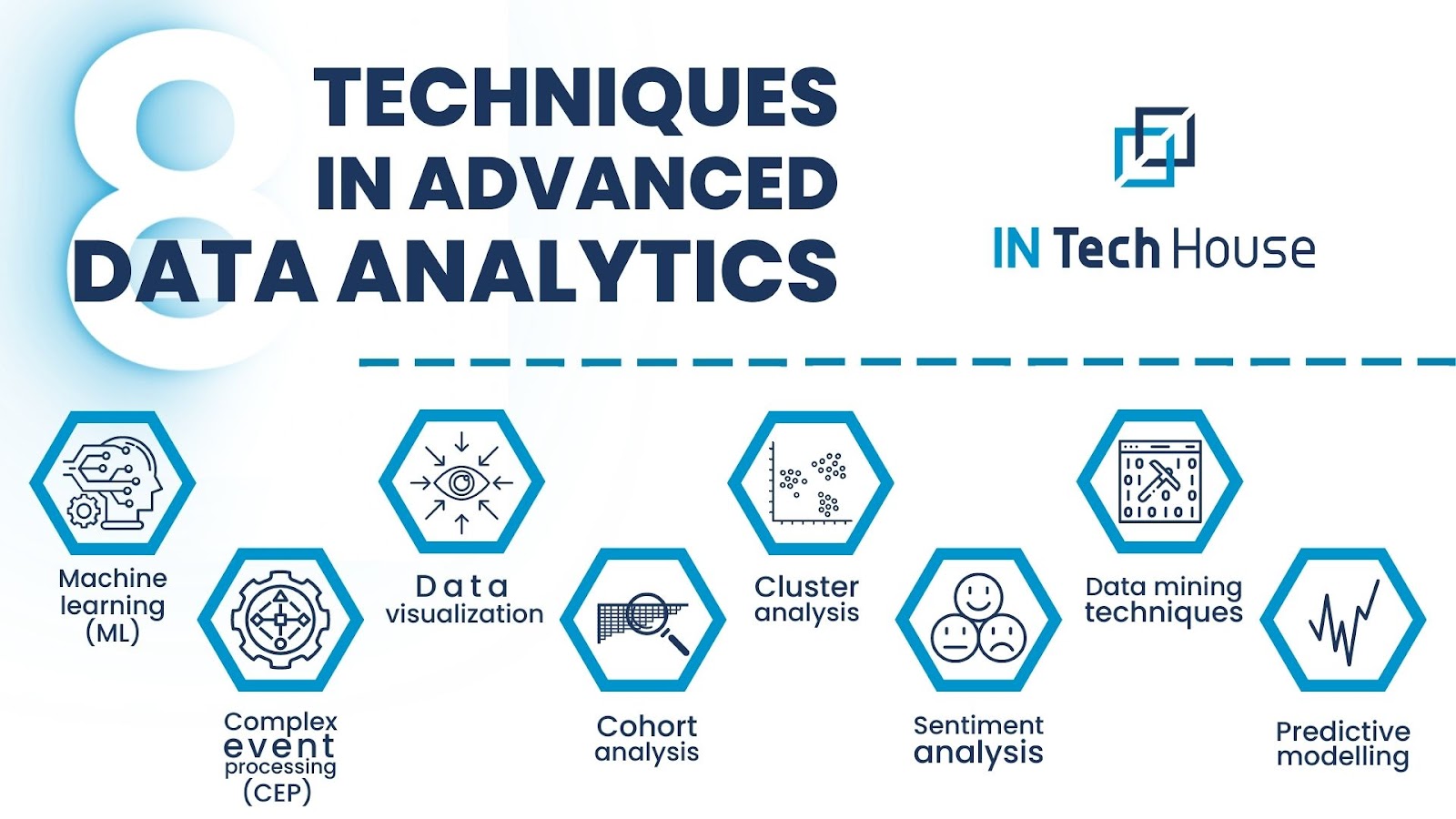
Data Analytics involves analyzing raw data to extract useful insights, identify patterns, and support decision-making. There are several key techniques used in Data Analytics, each serving different purposes. Descriptive Analytics focuses on summarizing past data to understand trends and patterns, often using tools like dashboards, reports, and data visualization techniques. Diagnostic Analytics goes a step further by identifying reasons behind trends using techniques like data mining, correlation analysis, and drill-down analysis. These techniques help organizations understand what happened and why it happened.
Another important technique is Predictive Analytics, which uses historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends. This includes techniques such as regression analysis, time series analysis, and classification models. Businesses use Predictive Analytics for demand forecasting, customer behavior predictions, and risk assessment. Similarly, Prescriptive Analytics provides actionable recommendations based on data insights, using optimization algorithms and AI-driven decision-making models. It helps businesses determine the best course of action, such as optimizing supply chain logistics or recommending personalized marketing strategies.
Advanced Data Analytics techniques include Sentiment Analysis, Text Analytics, and Real-time Analytics. Sentiment Analysis is commonly used in social media monitoring to analyze public opinions, while Text Analytics helps process large amounts of textual data for insights. Real-time Analytics enables immediate decision-making based on live data streams, often used in financial trading, fraud detection, and IoT applications. By leveraging these techniques, organizations can improve efficiency, enhance customer experience, and drive business growth. However, the success of Data Analytics depends on data quality, proper data governance, and the right use of analytical tools like Python, R, SQL, and cloud-based analytics platforms.
Click here for more information
Big Data tools and frameworks are essential for handling, processing, and analyzing vast amounts of structured and unstructured data efficiently. These tools help organizations store, manage, and derive insights from large datasets that traditional databases cannot handle. Hadoop is one of the most widely used frameworks, which utilizes a distributed storage system (HDFS) and parallel processing through MapReduce to handle large-scale data processing. Another popular framework is Apache Spark, which provides in-memory computing capabilities, making data processing much faster compared to Hadoop. Spark supports real-time analytics, machine learning, and graph processing, making it a preferred choice for modern data-intensive applications.
For data storage and management, NoSQL databases like Apache Cassandra, MongoDB, and HBase are commonly used. These databases offer scalability, flexibility, and high availability for managing unstructured and semi-structured data. Apache Kafka is another essential tool for real-time data streaming, widely used in applications requiring live data processing, such as financial transactions, IoT, and event-driven architectures. Elasticsearch is used for searching and analyzing large volumes of data efficiently, commonly used in log analytics and full-text search applications.
In the realm of Big Data analytics, tools like Apache Flink, Apache Storm, and Google BigQuery enable real-time data analysis and processing. Data visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio help in presenting insights in an understandable format. Machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and MLlib (Spark's ML library) play a significant role in predictive analytics and AI-driven insights. With the increasing demand for cloud-based Big Data solutions, platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer managed services like Amazon EMR, Google BigQuery, and Azure Synapse Analytics, making Big Data processing more accessible and scalable. These tools and frameworks collectively empower businesses to harness the full potential of Big Data for decision-making, automation, and innovation...............
Click here for more information

Big Data is transforming the way businesses and marketers operate by enabling data-driven decision-making, improving customer experiences, and optimizing business strategies. Companies collect vast amounts of data from various sources such as social media, websites, customer interactions, and IoT devices. This data is analyzed to understand customer behavior, market trends, and business performance. Predictive analytics helps businesses forecast sales, customer preferences, and demand fluctuations, allowing companies to plan strategies accordingly. For example, e-commerce platforms like Amazon use Big Data analytics to provide personalized recommendations based on a user's browsing and purchasing history, increasing customer engagement and sales.
In marketing, Big Data allows for hyper-personalization by segmenting customers based on their preferences, behavior, and demographics. Businesses use customer relationship management (CRM) tools integrated with Big Data analytics to track customer interactions, predict their needs, and tailor marketing campaigns. Programmatic advertising leverages Big Data to automate digital ad placements, ensuring that the right ads reach the right audience at the right time. Companies like Google and Facebook use Big Data-driven algorithms to optimize ad targeting, increasing conversion rates and return on investment (ROI). Sentiment analysis, which examines customer opinions and emotions from social media and online reviews, helps brands assess their reputation and adjust marketing strategies accordingly.
Big Data also enhances real-time decision-making in business operations. Retail companies optimize inventory management by analyzing sales patterns and demand predictions, reducing overstock and stock shortages. Financial institutions use Big Data to detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, improving security and customer trust. In supply chain management, data analytics enables businesses to monitor logistics, reduce costs, and improve delivery efficiency. Additionally, businesses use Big Data for competitor analysis, gaining insights into market trends and identifying opportunities for growth. As data-driven strategies continue to evolve, companies leveraging Big Data gain a competitive edge in delivering better customer experiences, improving efficiency, and driving revenue growth...............
Click here for more information

Big Data provides numerous advantages in business, healthcare, finance, and other industries, but it also raises significant ethical and security concerns. The massive collection and storage of data make privacy protection a critical issue. Organizations collect vast amounts of personal data from users, often without their explicit consent or clear understanding of how it will be used. Ethical concerns arise when companies misuse data for profit, sell user information to third parties, or fail to provide adequate transparency about data collection practices. For example, social media platforms and search engines track user activities to create targeted advertisements, raising concerns about informed consent and digital surveillance. Ensuring ethical data practices requires businesses to adopt data governance policies that promote transparency, fairness, and accountability in data handling.
Security is another major challenge in Big Data. Large datasets are attractive targets for cybercriminals, increasing the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and financial fraud. Many high-profile cyberattacks have compromised sensitive user information, including credit card details, medical records, and personal communications. Organizations must implement strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure access controls to protect stored and transmitted data. Additionally, anonymization and data masking techniques help safeguard user privacy by removing personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets. Businesses should also regularly conduct cybersecurity audits and risk assessments to identify and fix vulnerabilities in their data infrastructure.
Another ethical concern in Big Data is bias and discrimination in data processing. Algorithms trained on biased datasets can reinforce societal inequalities, leading to unfair outcomes in areas such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement. For example, biased AI models in hiring processes may unintentionally favor certain demographics while discriminating against others. To address this, organizations must adopt fair and responsible AI practices, ensuring that their algorithms are trained on diverse and representative data. Governments and regulatory bodies have also introduced laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) to hold businesses accountable for data privacy violations. As Big Data continues to grow, ensuring ethical data usage and strong security measures will be crucial in maintaining user trust and preventing misuse of sensitive information.
.........
Click here for more information

Comments