Quantum Applications & Future Trends
1. what is Quantum Applications & Future Trends?
Quantum Applications & Future Trends refer to the practical uses of quantum computing and quantum technologies in solving real-world problems across various industries. While quantum computing is still in its early stages, it holds immense potential for transforming fields such as cryptography, optimization, material science, machine learning, and drug discovery. By harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, quantum computers can perform certain types of calculations much faster than classical computers, which makes them particularly suited for complex problems that are otherwise infeasible for classical systems.
One of the most promising quantum applications is in quantum cryptography, specifically Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). This method offers the potential for unbreakable encryption by utilizing quantum mechanics to detect eavesdropping during the communication process. Additionally, quantum machine learning is another area where quantum computing can revolutionize data analysis and pattern recognition, enabling faster training of AI models and solving complex problems in less time. In optimization problems, quantum algorithms can enhance solutions in industries such as logistics, finance, and manufacturing, where finding the best possible solution from a large set of possibilities is critical. Quantum computing also has significant potential in material science, where simulating the properties of molecules and materials at the quantum level can lead to breakthroughs in creating more efficient solar cells, batteries, and other technologies.
As for future trends, quantum computing is expected to evolve rapidly over the coming years. In the short term, quantum hardware development will continue to advance, with companies like Google, IBM, and Rigetti aiming to build more powerful and stable quantum processors. These processors will increase the number of qubits and improve the fidelity of quantum operations, bringing quantum computing closer to real-world practical applications. In parallel, quantum software and quantum algorithms will be developed and optimized for specific use cases, making it easier to harness the power of quantum systems without requiring deep expertise in quantum mechanics.
2.Quantum in Drug Discovery
Quantum in Drug Discovery
holds the potential to revolutionize how pharmaceuticals are developed by enabling faster and more accurate simulations of molecular interactions. One of the primary challenges in drug discovery is understanding how different molecules interact at the atomic and subatomic levels, which is essential for identifying potential drug candidates. Traditional methods, such as molecular dynamics simulations, rely on classical computing and can take significant time and computational resources to simulate even small molecules. Quantum computing, with its ability to process vast amounts of data simultaneously using principles like superposition and entanglement, can drastically reduce the time required to model complex chemical reactions and molecular interactions.
One of the most promising applications of quantum computing in drug discovery is in quantum chemistry. Quantum computers can simulate the behavior of molecules and atoms with much higher accuracy than classical computers, thanks to their ability to directly model quantum states. This ability allows quantum computers to perform simulations of molecular interactions that are beyond the capabilities of classical systems. This could lead to more accurate predictions of how a drug molecule will interact with a target protein or enzyme, enabling the identification of promising drug candidates much more quickly and efficiently. Additionally, quantum computing can help in understanding protein folding, a crucial process in biology that influences many diseases, including Alzheimer’s and cancer. By simulating the folding of proteins at the quantum level, researchers can gain insights into how these proteins might malfunction in certain diseases, leading to better-targeted therapies.
In the future, quantum algorithms may also help in the design of new drugs by analyzing vast chemical spaces that classical methods cannot explore effectively. The ability to search through millions of molecular combinations in a fraction of the time it would take on classical computers could expedite the development of new therapies. Moreover, quantum computing could improve personalized medicine by enabling more precise predictions of how a patient’s unique genetic makeup will interact with specific drugs, leading to better treatment outcomes with fewer side effects. However, despite the immense potential, practical use of quantum computing in drug discovery still faces challenges, including the need for scalable, fault-tolerant quantum hardware and the development of quantum algorithms that can handle real-world biological data. As these hurdles are overcome, quantum computing will likely become a key tool in the next generation of drug discovery and personalized medicine.

3.Quantum in Financial Modeling
Quantum in Financial Modeling
holds the potential to revolutionize the way financial institutions, investment firms, and analysts approach risk management, portfolio optimization, and market predictions. Traditional financial models rely on classical computing, which can become computationally expensive and inefficient when dealing with large datasets, complex calculations, and real-time market fluctuations. Quantum computing, with its ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data simultaneously using quantum bits (qubits), offers a new way to solve these complex financial problems much more efficiently. By leveraging quantum algorithms, financial models could be more accurate, faster, and able to process more variables at once, enabling quicker decision-making and potentially higher profits.
One key area where quantum computing is expected to have a significant impact is optimization. In finance, optimization problems such as portfolio management, asset allocation, and option pricing require finding the best possible solution from a large set of possibilities. Classical computers struggle to handle these problems at scale, especially when the number of assets or variables increases. Quantum algorithms, such as quantum annealing and Grover’s search algorithm, can search through large solution spaces exponentially faster than classical methods. This could allow investment firms to optimize portfolios, balance risks, and calculate returns with greater precision and speed. For example, quantum computing could help optimize hedging strategies or determine the optimal mix of investments across multiple assets, factoring in real-time market data and varying risk factors.
Additionally, quantum computing can improve risk analysis and pricing models. Financial institutions rely heavily on stochastic models to predict market behavior and evaluate the risk of financial instruments like derivatives. Classical approaches to modeling these risks can be slow and prone to inaccuracies, particularly when trying to simulate scenarios with multiple variables. Quantum computing can simulate more complex scenarios, offering faster and more accurate pricing for derivatives, options, and bonds. Quantum algorithms could also enhance Monte Carlo simulations, which are used to assess risk by running multiple simulations of financial models to understand possible outcomes. Quantum computing can exponentially speed up these simulations, allowing for more frequent and granular risk assessments. As quantum technology matures, it will likely become an essential tool for improving financial modeling, providing new ways to understand, predict, and manage financial markets with much higher accuracy and efficiency than classical systems.

4.Quantum in Material Science
Quantum in Material Science
is poised to significantly impact the way we design, simulate, and understand materials at the atomic and molecular levels. Traditional methods of simulating material properties, like classical computing and density functional theory (DFT), are limited when it comes to accurately modeling complex materials, especially when dealing with large molecules, exotic materials, or quantum effects. Quantum computers, however, operate using the principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, which allow them to model atomic and subatomic interactions with far greater accuracy than classical systems. This ability to simulate quantum systems at scale could lead to breakthroughs in material science, enabling the design of new materials with unprecedented properties, from superconductors to novel nanomaterials.
One of the most promising applications of quantum computing in material science is in the development of new materials for energy storage and generation. Quantum computers can simulate the behavior of molecules and atoms in complex materials, making it easier to identify new materials with properties such as high energy efficiency, superconductivity, or resistance to wear and tear. For example, quantum computing could play a crucial role in designing better batteries by accurately simulating the interactions of atoms and molecules within battery materials, leading to improvements in energy density, charging speed, and durability. Similarly, quantum simulations could enable the development of high-performance catalysts for chemical reactions, which are essential in processes like hydrogen production or carbon capture. These advancements could accelerate the transition to more sustainable and energy-efficient technologies.
In the realm of quantum materials—materials that exhibit unique quantum properties—quantum computing could help design materials for future technologies, such as quantum computers themselves. Quantum materials, including topological insulators, superconductors, and quantum dots, are expected to play a key role in the next generation of computing and communication technologies. Quantum computing can help researchers understand the behavior of these materials at the quantum level, revealing new insights into their properties and enabling the engineering of new materials with specific quantum behaviors. For instance, topological quantum materials, which exhibit robust edge states immune to defects, could be crucial for building more stable quantum processors. In summary, quantum computing has the potential to accelerate material science research by enabling the design, discovery, and understanding of advanced materials with properties that are currently difficult or impossible to model with classical computers. This could lead to innovations in energy, manufacturing, electronics, and many other fields.

5.Quantum Cloud Services
Quantum Cloud Services
refer to cloud-based platforms that provide access to quantum computing resources and tools over the internet. These services allow individuals, researchers, and businesses to leverage the power of quantum computing without needing to own or maintain the complex hardware required for quantum computations. By offering remote access to quantum processors and quantum simulators, these cloud platforms make it easier to experiment with quantum algorithms, develop applications, and explore quantum computing's potential across various industries. Key quantum cloud services are typically provided by leading tech companies, such as IBM, Microsoft, Amazon, and Google, which have invested in developing quantum computing infrastructure and ecosystems.
One of the key advantages of quantum cloud services is the ability to scale quantum computing efforts without needing specialized hardware. Traditional quantum computers require highly controlled environments, like cryogenic cooling systems for superconducting qubits or vacuum chambers for trapped ions. This makes maintaining a quantum computer on-premises prohibitively expensive and technically challenging. Quantum cloud services solve this by providing access to these advanced systems remotely, allowing users to run experiments, perform calculations, and explore quantum algorithms without needing to manage the underlying infrastructure. Additionally, cloud platforms often offer hybrid solutions, where users can combine classical computing power with quantum computing resources, enabling them to solve complex problems that require both types of computational power.
Furthermore, quantum cloud platforms often provide an ecosystem of quantum programming languages, simulators, and development tools that simplify the learning curve for quantum computing. For instance, IBM offers the Qiskit framework for developing quantum programs, while Microsoft provides Azure Quantum, a cloud service with a variety of quantum solvers. These services enable users to build, test, and run quantum algorithms on real quantum hardware or simulators, offering an environment for research and development. Quantum cloud services are not only beneficial for academic researchers but are also opening doors for industries like finance, healthcare, energy, and material science to experiment with quantum solutions. As quantum computing continues to evolve, these cloud services will play a pivotal role in accelerating the accessibility and adoption of quantum technologies.

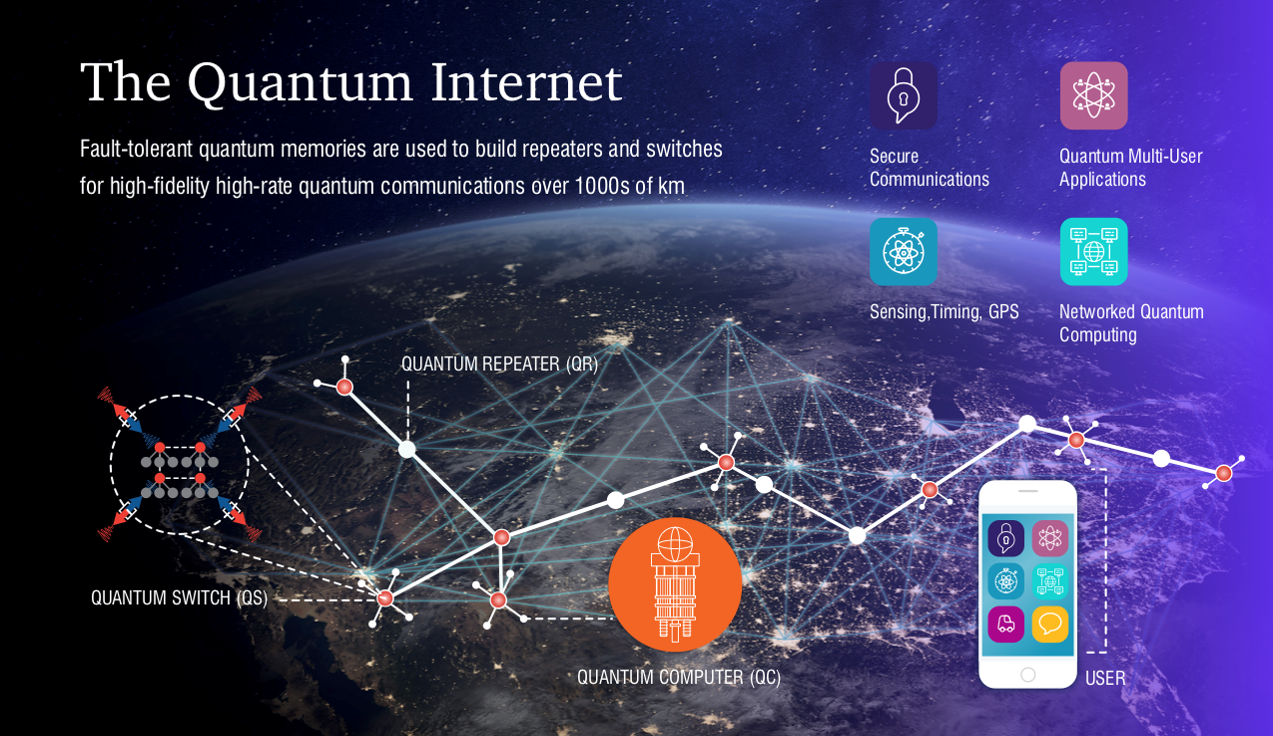
6.Quantum Internet
Quantum Internet
it is an emerging concept that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to create a new type of internet capable of transmitting information with enhanced security, speed, and efficiency. Unlike the classical internet, which relies on traditional communication methods like fiber-optic cables and electromagnetic signals, the quantum internet leverages quantum bits, or qubits, and phenomena like quantum entanglement and quantum superposition to enable fundamentally new capabilities. One of the most significant advantages of a quantum internet is its ability to provide ultra-secure communication, as quantum information cannot be measured or intercepted without disturbing the system, a property known as the no-cloning theorem.
A core feature of the quantum internet is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), a technique that allows two parties to securely share encryption keys over long distances. In classical communication, eavesdropping on the transmission of data can compromise security. However, with QKD, any attempt to intercept the quantum communication would disturb the quantum state, alerting both parties to the presence of an intruder. This ensures that the transmission of sensitive data, such as financial transactions or personal information, is secure against cyberattacks, even from the most advanced hacking techniques. Additionally, the quantum internet could enable quantum teleportation, which would allow the transfer of quantum information between distant locations, further expanding the possibilities for secure communication networks.
Beyond security, the quantum internet could also lead to advancements in distributed quantum computing and quantum-enhanced networking. In this scenario, quantum computers at different locations could be connected, allowing them to share and process quantum information across vast distances. This would enable the creation of highly efficient, collaborative quantum networks, improving computing power and enabling complex quantum simulations and algorithms that are not feasible on classical systems. Moreover, the quantum internet could facilitate quantum cloud computing, where users could access remote quantum computing resources securely over the network. Although the quantum internet is still in its early stages, and many technological and infrastructural challenges remain, it has the potential to revolutionize communication, networking, and computing in the future by providing a level of security and processing power far beyond what is possible today.
7.Ethical Concerns of Quantum Computing
Ethical Concerns of Quantum Computing
are a critical area of discussion as this technology continues to advance. While quantum computing promises significant breakthroughs in fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and optimization, it also introduces new challenges and risks that need to be addressed. One of the most pressing ethical issues is related to data privacy and security. Quantum computers have the potential to break traditional encryption methods, such as RSA, which rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. This means that once powerful quantum computers are widely available, they could potentially decrypt sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, and government communications, that are currently considered secure. The ethical dilemma here lies in the fact that, while quantum computing could revolutionize cybersecurity with quantum-safe encryption techniques, it could also expose existing data to unprecedented risks, making it imperative to develop new cryptographic protocols before quantum computers become fully operational.
Another ethical concern revolves around the impact of quantum computing on jobs and the economy. Quantum computing has the potential to automate complex tasks and solve problems that are currently too difficult for classical computers to handle. While this could lead to innovations and efficiency gains, it might also disrupt industries and labor markets. Jobs in sectors like finance, healthcare, and logistics could be displaced by quantum algorithms that optimize decision-making or perform advanced simulations. Moreover, the high cost of quantum technology and the expertise required to operate and maintain quantum systems could create a digital divide, where only a small group of technologically advanced countries or corporations can access and benefit from quantum computing. This raises questions about equity and fairness, as it could exacerbate existing socioeconomic disparities.
Finally, there are concerns about the misuse of quantum computing for malicious purposes. With its potential to break encryption and access sensitive data, quantum computing could be used by bad actors, including hackers, cybercriminals, or even nation-states, to launch more sophisticated cyberattacks. Additionally, quantum-enhanced AI could be used to automate and accelerate cyberattacks, making it even harder to defend against malicious activities. There's also the risk of quantum technologies being used in unethical ways in fields like surveillance, where quantum-powered systems could be employed to invade privacy on an unprecedented scale. These ethical issues highlight the importance of regulating the development and use of quantum technologies, ensuring that the benefits of quantum computing are distributed fairly while minimizing its potential for harm.

8.Future of Quantum Technologies
Future of Quantum Technologies promises to revolutionize various industries by harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum computing, one of the most anticipated advancements, aims to perform complex calculations much faster than classical computers. As research progresses, quantum computers could solve problems in cryptography, drug discovery, climate modeling, and financial modeling that are currently impossible or would take years using traditional systems. Companies like Google, IBM, and Microsoft are investing heavily in developing quantum processors, improving qubit stability, and enhancing error correction to make quantum computing more practical and accessible.
Beyond computing, quantum communication holds promise for ultra-secure data transfer using principles like quantum key distribution (QKD). This technology makes eavesdropping nearly impossible by using the quantum property of entanglement to detect any interception attempts. Countries like China are already leading in quantum communication by launching quantum satellites and establishing secure networks. In the future, global quantum communication networks may become the standard for protecting sensitive information and securing digital infrastructures against advanced cyber threats.
Quantum sensing is another emerging area with transformative potential. It offers unparalleled accuracy in measuring physical phenomena, including magnetic fields, gravity, and time. This could lead to breakthroughs in medical imaging, earthquake prediction, navigation, and defense applications. As quantum technology matures, industries will adopt these advanced sensing capabilities to improve performance and safety. Despite current challenges like scalability, error correction, and environmental stability, continuous research suggests that quantum technologies will play a critical role in shaping the future of computing, security, and scientific discovery over the next few decades.

Future of Quantum Technologies promises to revolutionize various industries by harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum computing, one of the most anticipated advancements, aims to perform complex calculations much faster than classical computers. As research progresses, quantum computers could solve problems in cryptography, drug discovery, climate modeling, and financial modeling that are currently impossible or would take years using traditional systems. Companies like Google, IBM, and Microsoft are investing heavily in developing quantum processors, improving qubit stability, and enhancing error correction to make quantum computing more practical and accessible.
Beyond computing, quantum communication holds promise for ultra-secure data transfer using principles like quantum key distribution (QKD). This technology makes eavesdropping nearly impossible by using the quantum property of entanglement to detect any interception attempts. Countries like China are already leading in quantum communication by launching quantum satellites and establishing secure networks. In the future, global quantum communication networks may become the standard for protecting sensitive information and securing digital infrastructures against advanced cyber threats.
Quantum sensing is another emerging area with transformative potential. It offers unparalleled accuracy in measuring physical phenomena, including magnetic fields, gravity, and time. This could lead to breakthroughs in medical imaging, earthquake prediction, navigation, and defense applications. As quantum technology matures, industries will adopt these advanced sensing capabilities to improve performance and safety. Despite current challenges like scalability, error correction, and environmental stability, continuous research suggests that quantum technologies will play a critical role in shaping the future of computing, security, and scientific discovery over the next few decades.

Comments