Internet of Things (IoT)
Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet without human intervention.
Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet without human intervention.
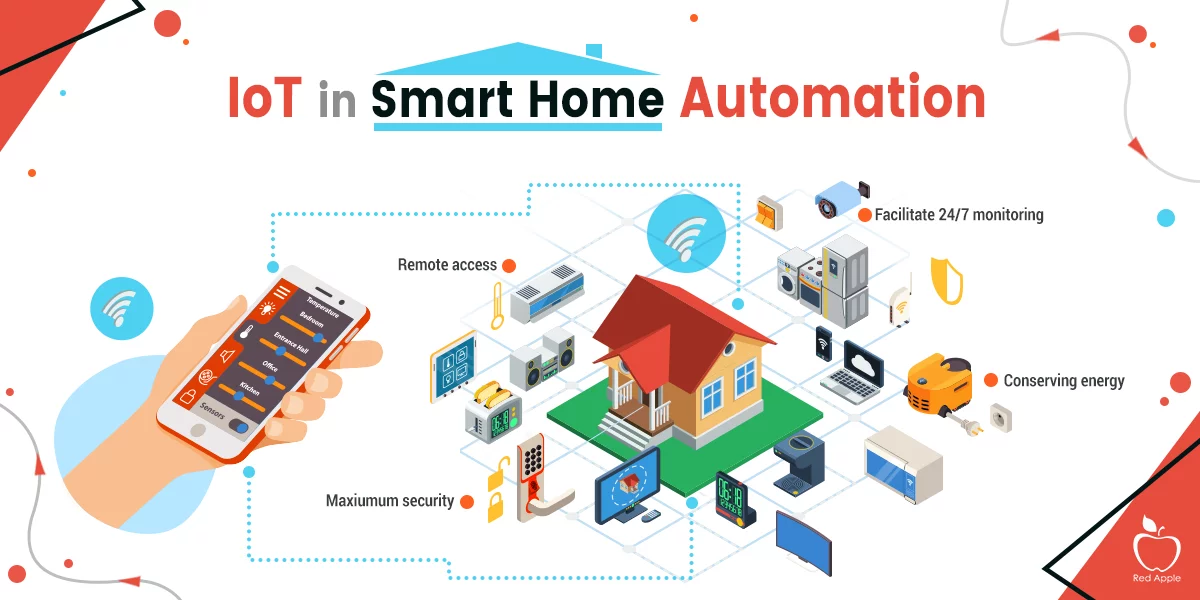
Smart home automation is transforming modern living by integrating Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing to create intelligent and automated home environments. With smart home technology, users can remotely control devices such as lighting, thermostats, security cameras, appliances, and entertainment systems through smartphones, voice assistants, or automation hubs. Popular AI-powered assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri enable users to manage their homes with simple voice commands, making daily tasks more convenient and efficient. Smart homes also feature motion sensors, automated lighting, and smart locks, improving both security and energy efficiency.
One of the biggest benefits of smart home automation is energy management and cost savings. Smart thermostats, such as Google Nest and Ecobee, learn user preferences and adjust temperatures accordingly, reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Smart lighting systems, like Philips Hue and LIFX, allow users to schedule lights to turn on or off automatically, optimizing electricity usage. Additionally, smart plugs and power strips help monitor energy consumption, allowing homeowners to control appliances remotely and prevent energy waste. These innovations contribute to eco-friendly living by reducing the overall carbon footprint of households.
Security is another crucial aspect of smart home automation. Advanced smart security systems, such as Ring, Arlo, and Wyze, offer real-time surveillance, facial recognition, and motion detection to keep homes safe. Smart locks and video doorbells provide remote access control, allowing homeowners to grant entry to visitors or delivery personnel even when they are away. Moreover, smart smoke detectors, water leak sensors, and AI-powered home monitoring systems provide real-time alerts, preventing potential disasters. As technology continues to evolve, smart home automation will become even more sophisticated, offering seamless integration, greater customization, and enhanced convenience for modern living......
Click here for more information
Industrial IoT (IIoT) refers to the application of Internet of Things (IoT) technology in industrial settings, such as manufacturing, energy, logistics, and agriculture. IIoT enables the connection of machines, sensors, and cloud computing systems, allowing real-time data collection, analysis, and automation. This technology helps industries improve efficiency, productivity, and safety by enabling predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and automated control systems. By using AI, machine learning, and big data analytics, IIoT helps businesses reduce operational costs and optimize resource utilization.
One of the key advantages of IIoT is predictive maintenance, where sensors continuously monitor machine performance and detect potential failures before they happen. This minimizes downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of equipment. For example, in manufacturing, IIoT-enabled robots and machines can self-diagnose issues and request repairs, ensuring smooth operations. In energy industries, IIoT helps monitor power grids, oil pipelines, and wind turbines, improving energy efficiency and preventing breakdowns. Smart factories, also known as Industry 4.0, leverage IIoT to create fully automated and interconnected production systems.
Security and data privacy are major challenges in IIoT, as industrial systems become more interconnected. Cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and hacking can disrupt operations and cause financial losses. To counter these risks, industries implement blockchain technology, AI-driven threat detection, and advanced encryption to secure IIoT networks. As IIoT continues to evolve, it will drive innovation in various sectors, enabling self-operating factories, AI-powered logistics, and highly efficient industrial ecosystems, ultimately reshaping the future of industry...........
Click here for more information

Wearable technology refers to electronic devices that can be worn on the body to monitor, track, and enhance various aspects of daily life. These devices are embedded with sensors, microprocessors, and connectivity features, allowing users to collect real-time data and interact with digital systems. Common wearable devices include smartwatches, fitness trackers, smart glasses, and smart clothing. They are widely used in healthcare, sports, communication, and entertainment. With advancements in AI and IoT, wearable devices have become more intelligent, capable of analyzing biometric data, detecting health conditions, and even assisting with augmented reality experiences.
One of the most significant applications of wearable technology is in health and fitness tracking. Devices like smartwatches and fitness bands track metrics such as heart rate, steps, sleep patterns, blood oxygen levels, and calories burned. Some advanced wearables can even detect irregular heart rhythms, monitor blood pressure, or predict potential health risks using AI-driven analytics. Medical wearables, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) for diabetics and smart ECG monitors, provide real-time health insights to users and doctors. Wearable devices also support mental well-being by tracking stress levels and providing guided meditation or relaxation exercises.
Beyond health, wearable technology is transforming communication, work, and entertainment. Smart glasses with AR (Augmented Reality) overlay digital information onto the real world, enhancing navigation, education, and industrial training. Wearable exoskeletons help workers lift heavy objects safely, reducing workplace injuries. In sports, athletes use smart clothing with embedded sensors to track performance and improve training. With continuous advancements, wearable technology is expected to become more seamless, powerful, and integrated with AI, leading to innovations such as brain-computer interfaces, AI-powered assistants, and even implantable smart devices in the future...........
Click here for more information

The Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare refers to the integration of smart devices, sensors, and cloud-based platforms to enhance medical services, patient care, and hospital management. IoT-enabled medical devices collect real-time health data, allowing doctors and healthcare professionals to monitor patients remotely, track vital signs, and detect early warning signs of diseases. Examples of IoT in healthcare include wearable health monitors, smart insulin pumps, remote patient monitoring systems, and connected inhalers. These devices improve patient outcomes by providing continuous health tracking and alerting medical professionals in case of emergencies.
One of the key applications of IoT in healthcare is Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM). IoT devices such as wearable ECG monitors, smart blood pressure cuffs, and continuous glucose monitors allow patients, especially those with chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, or heart conditions, to be monitored from home. The collected data is transmitted to healthcare providers, enabling early detection of health issues and reducing the need for frequent hospital visits. Smart hospital beds, IoT-enabled wheelchairs, and AI-powered virtual nurses also improve patient care by automating routine tasks and enhancing hospital efficiency.
IoT is also revolutionizing hospital management and medical supply chain logistics. Smart inventory systems track the availability of critical medicines, medical equipment, and vaccines in real-time, preventing shortages or wastage. IoT-powered disinfection robots and air quality sensors help maintain hospital hygiene and reduce infections. Additionally, IoT enhances surgical precision with robot-assisted surgeries, where connected robotic systems assist doctors in performing complex procedures with higher accuracy. As IoT technology advances, it is expected to make healthcare more personalized, efficient, and accessible, ultimately saving lives and improving medical outcomes...........
Click here for more information

The rapid adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) has brought numerous benefits, but it has also introduced significant security risks. Since IoT devices are interconnected and collect vast amounts of sensitive data, they become prime targets for cyberattacks. One major challenge is the lack of strong security protocols in many IoT devices. Manufacturers often prioritize affordability and ease of use over security, leading to devices with weak encryption, default passwords, and outdated software. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by hackers to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or launch large-scale cyberattacks.
Another critical challenge is the high risk of Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. Cybercriminals can hijack poorly secured IoT devices and turn them into a botnet to flood networks with massive amounts of traffic, causing downtime and disruption. A well-known example is the Mirai botnet attack, where thousands of compromised IoT devices were used to disable major websites and services. Additionally, data privacy concerns arise as IoT devices continuously collect personal information, including health records, location data, and home security footage. If these devices are not properly secured, sensitive data can be leaked or misused.
IoT security is also challenged by difficulty in updating and patching vulnerabilities. Unlike traditional computers and smartphones, many IoT devices lack automatic update mechanisms, making them vulnerable to newly discovered threats. Once a device is deployed, it may remain exposed for years without receiving security patches. To address these challenges, strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular software updates, and network segmentation must be implemented. Governments and organizations are also working on creating IoT security standards to ensure safer deployments in smart homes, healthcare, industrial systems, and critical infrastructures.
.........
Click here for more information

Comments