Cloud Security
1. What is Cloud Security?

Cloud Security Cloud security refers to the practices, technologies, and policies designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments. As businesses increasingly move their operations to the cloud, ensuring the safety of sensitive data is critical. Cloud security involves safeguarding data from unauthorized access, breaches, and loss. It includes measures such as encryption, access control, identity management, and regular audits to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Cloud service providers (CSPs) also implement advanced security protocols to protect against cyber threats, ensuring that customer data remains secure in transit and at rest..
Key components of cloud security include data encryption, identity and access management (IAM), network security, and disaster recovery. Data encryption ensures that information is scrambled and only accessible to authorized users with the correct keys. IAM systems restrict access to sensitive resources based on user roles, enhancing security. Network security includes firewalls and virtual private networks (VPNs) to protect against external threats. Additionally, disaster recovery ensures that data is backed up and can be restored in case of data loss, ensuring business continuity. These measures are critical for protecting against cyberattacks like data breaches, DDoS attacks, and malware.
Compliance with industry regulations is another crucial aspect of cloud security. Organizations using cloud services must adhere to standards such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and ISO/IEC 27001. Cloud providers offer tools to help organizations meet these legal and regulatory requirements while ensuring transparency and data protection. As cloud adoption grows, multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud environments require more advanced security strategies. Implementing robust cloud security not only protects data but also builds trust with customers and partners while reducing the risk of financial and reputational damage.
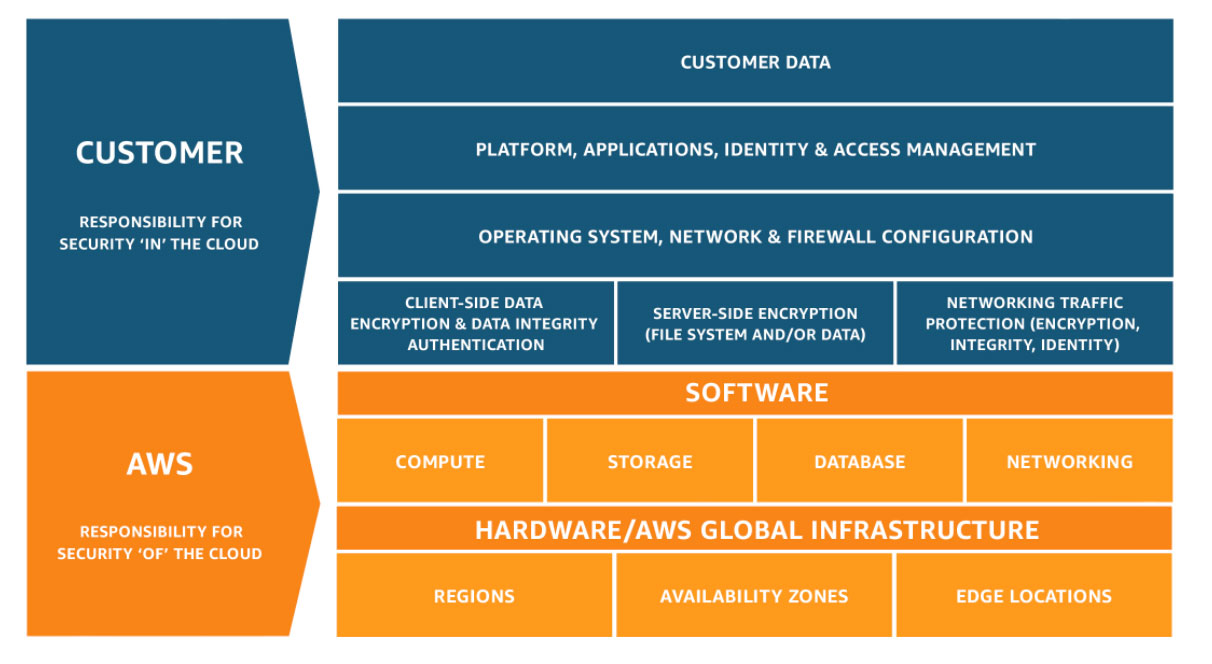
2. Shared Responsibility Model
Shared Responsibility Model cloud security defines the division of security responsibilities between the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer. This model ensures that both parties understand and manage their specific security duties. The cloud provider is responsible for securing the infrastructure, including physical servers, storage, and networking. Meanwhile, the customer is responsible for securing their data, applications, and user access. This approach ensures a collaborative effort to maintain a secure cloud environment.
In IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), the provider secures the physical infrastructure, while customers manage operating systems, applications, and data. For PaaS (Platform as a Service), the provider handles the platform, including middleware and runtime, while customers secure their applications and data. In SaaS (Software as a Service), the provider manages everything from infrastructure to software, and customers focus on securing data and managing user access. Each cloud model requires both parties to work together to maintain data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
A key aspect of the shared responsibility model is compliance and risk management. Cloud providers offer tools like encryption, firewalls, and identity management to help customers fulfill their security obligations. Customers must implement access controls, monitor user activity, and manage data privacy. Understanding and adhering to the shared responsibility model helps organizations reduce security risks, achieve regulatory compliance, and protect sensitive information. Both parties must actively engage in maintaining security to ensure a safe and reliable cloud environment.
3. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) is a security solution that acts as an intermediary between users and cloud service providers to enforce security policies and protect data. It provides organizations with visibility, control, and protection over data in cloud environments. CASBs help monitor user activities, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure compliance with regulations. They work across different cloud service models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, ensuring that data remains secure whether it is stored, transferred, or processed
CASBs offer four primary functions: visibility, data security, threat protection, and compliance. They provide visibility into how employees use cloud services, including detecting unsanctioned or "shadow IT" applications. Data security is maintained through encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP) policies. Threat protection involves detecting and mitigating risks such as malware, unauthorized access, and insider threats. Compliance ensures that organizations follow legal and industry regulations by monitoring and controlling data usage in the cloud.
PImplementing a CASB is essential for businesses adopting cloud services. It helps enforce security policies, monitor user behavior, and detect anomalies that may indicate a security breach. CASBs also integrate with identity management systems and endpoint security tools to provide a unified security framework. By using a CASB, organizations can balance the flexibility of the cloud while maintaining data privacy, user access control, and regulatory compliance
.webp)
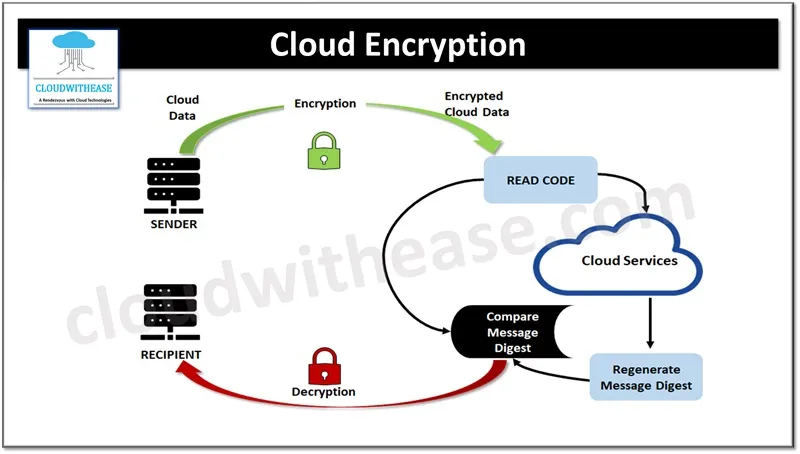
4.Cloud Encryption
Cloud Encryptionis the process of converting data into a coded format before storing or transmitting it in the cloud. It ensures that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access by making it unreadable without the correct decryption key. Cloud encryption is used for securing data at rest (stored data), in transit (data being transferred), and in use (actively processed data). This helps businesses safeguard confidential information such as customer records, intellectual property, and financial data from cyber threats and data breaches.
Encryption in the cloud involves using advanced algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman). AES-256, for example, is a widely used encryption standard that provides strong protection by encoding data with a 256-bit key. Cloud providers typically offer server-side encryption (SSE), where data is encrypted on their servers, and client-side encryption (CSE), where data is encrypted before it reaches the cloud. Both methods ensure that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties, it remains unintelligible.
One of the key challenges in cloud encryption is managing encryption keys securely. Organizations must decide whether to let the cloud provider manage the keys or maintain their own encryption key management system (KMS). Using bring-your-own-key (BYOK) or hold-your-own-key (HYOK) approaches gives businesses more control over their encrypted data. Effective cloud encryption not only protects privacy and ensures compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) but also reduces the risk of data leaks and cyberattacks.
5.Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Identity & Access Management (IAM) is a framework of policies and technologies used to ensure that the right individuals and devices have the appropriate access to technology resources. It helps organizations control who can access what, ensuring only authorized users can view or modify sensitive information. IAM involves managing user identities, authenticating users, and defining roles and permissions to enforce access controls. This system is essential for maintaining security, compliance, and data privacy in modern IT environments, including cloud services and on-premises infrastructure.
Key components of IAM include user authentication, authorization, and user provisioning. Authentication verifies a user's identity through methods like passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), or biometrics. Authorization determines what resources the authenticated user is allowed to access, using role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC). User provisioning involves creating, managing, and deactivating user accounts as employees join, change roles, or leave the organization. This lifecycle management reduces the risk of unauthorized access and insider threats.
Modern IAM solutions often incorporate advanced features like Single Sign-On (SSO) and Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). SSO allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, improving user experience and reducing password-related vulnerabilities. Zero Trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," requiring continuous identity verification even for internal users. Effective IAM implementation protects sensitive data, supports regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), and minimizes the risk of data breaches by ensuring that access is strictly controlled and audited.

6. Cloud Security Best Practices
Cloud Security Best Practices are essential for protecting data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments. These practices help mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability. One key practice is implementing strong access controls using Identity and Access Management (IAM). This ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive data and resources. Utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Another critical best practice is encrypting data both in transit and at rest. This protects sensitive information from interception and unauthorized access. Organizations should use cloud-native encryption tools or third-party solutions to secure data. Additionally, regular backups are vital for data recovery in case of accidental deletion, ransomware attacks, or system failures. Automated and encrypted backups stored in a separate location ensure data can be restored without compromising security.
Continuous monitoring and logging is also a crucial cloud security practice. Organizations should track user activities, network traffic, and system events to detect anomalies and potential threats in real time. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools help collect and analyze logs, offering insights into suspicious activities. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments identify weaknesses, ensuring systems remain updated and compliant with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. By combining these best practices, organizations can strengthen their cloud security posture and protect critical assets.

7. Serverless Security
Serverless Security focuses on protecting applications running on serverless architectures, where cloud providers handle infrastructure management while developers focus on writing code. Since there are no traditional servers to manage, the main security challenge lies in securing the application code and protecting sensitive data. It is crucial to ensure that code is free from vulnerabilities by using secure coding practices, performing regular code reviews, and scanning for security flaws. Additionally, controlling access through Identity and Access Management (IAM) ensures that functions have only the permissions they need, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Another key aspect of serverless security is data protection. Sensitive information like API keys and database credentials should never be hard-coded into functions. Instead, use environment variables and cloud-native secrets management to store and encrypt critical data securely. Input validation is also essential to prevent injection attacks, where malicious inputs can exploit vulnerabilities in the code. Regular dependency checks and updates for third-party libraries help protect against known vulnerabilities that could compromise the serverless environment.
Monitoring and logging play a vital role in detecting and responding to security incidents. Implementing real-time logging and threat detection helps identify unusual activities, such as unexpected function triggers or failed authentication attempts. Cloud providers offer tools like AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Operations for comprehensive monitoring. Conducting regular security assessments and adopting best practices, such as the principle of least privilege and function-level isolation, enhances overall security and ensures compliance with industry standards.

8. Cloud Data Breaches
Cloud Data Breaches occur when unauthorized parties access, steal, or expose sensitive information stored in cloud environments. These breaches can result from misconfigured cloud settings, weak passwords, or vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure. Misconfigurations, such as open storage buckets or public databases, are a common cause of data leaks. Weak or reused passwords increase the risk of unauthorized access, especially when multi-factor authentication (MFA) is not enforced. Additionally, inadequate encryption during data transmission and storage can expose confidential data to malicious actors.
Another major cause of cloud data breaches is insider threats. Employees or contractors with access to sensitive information may unintentionally or maliciously expose data. Phishing attacks targeting cloud service credentials can also compromise accounts, leading to unauthorized access. Furthermore, insufficient Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies, such as over-permissioned roles, make it easier for attackers to move laterally within a cloud environment once they gain access. Unpatched software and vulnerable APIs can also become entry points for attackers to exploit.
To mitigate cloud data breaches, organizations should implement strong access controls, enforce least privilege principles, and use MFA for all user accounts. Regularly auditing and monitoring cloud configurations helps identify and fix security gaps. Encrypting data both in transit and at rest ensures that even if data is accessed, it remains unreadable. Adopting Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) can provide an additional layer of security by monitoring user activity and enforcing security policies. Continuous employee training and incident response planning further reduce the risk and impact of cloud data breaches.

Comments