Big Data in Business & Marketing
1. what is Big Data in Business & Marketing?

Big Data in Business & Marketing plays a transformative role by providing organizations with actionable insights that enhance decision-making, improve customer experiences, and optimize business operations. In marketing, big data allows businesses to analyze large volumes of customer information, including purchase history, social media interactions, and web browsing behavior. This data helps marketers understand customer preferences and trends, allowing for the creation of personalized campaigns. By using tools like predictive analytics and machine learning, businesses can forecast customer behaviors and anticipate needs, ultimately increasing the effectiveness of their marketing strategies.
One of the key benefits of big data in business and marketing is customer segmentation. By analyzing data from various sources, such as customer demographics, online behavior, and transaction data, businesses can categorize their audience into distinct segments. This allows for more targeted marketing efforts, ensuring that messages reach the right people at the right time. Additionally, real-time analytics enable businesses to adapt marketing strategies on the fly, adjusting offers, promotions, or campaigns based on current consumer activity. This agility improves engagement and conversion rates while also boosting customer loyalty by providing a more personalized experience.
Furthermore, big data empowers businesses to measure the success of their marketing campaigns through detailed analytics. By tracking metrics such as website traffic, conversion rates, and social media engagement, companies can gain a deeper understanding of what resonates with their audience. This data-driven approach not only leads to more efficient marketing efforts but also helps organizations identify new revenue opportunities, optimize pricing strategies, and improve their products or services. In the competitive landscape of today’s business world, leveraging big data enables businesses to stay ahead of the curve and maintain a significant edge over competitors.
2.Customer Segmentation
Customer Segmentation
is the process of dividing a customer base into distinct groups or segments based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, preferences, and purchasing patterns. This segmentation allows businesses to tailor their marketing strategies, products, or services to meet the specific needs of each group, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and increasing sales. Common segmentation strategies include demographic segmentation (age, gender, income), geographic segmentation (location), psychographic segmentation (lifestyle, values), and behavioral segmentation (buying habits, product usage).
By using big data analytics and machine learning algorithms, businesses can create more accurate and granular customer segments. These tools analyze vast amounts of customer data collected from various sources, including website interactions, social media activity, transaction history, and customer feedback. Advanced segmentation techniques, such as cluster analysis, allow businesses to identify patterns and correlations in the data that may not be immediately apparent. This enables companies to go beyond basic demographic data and target customers based on more specific preferences and behaviors.
Customer segmentation also helps in personalizing marketing efforts. For example, a retail brand might create personalized email campaigns based on previous purchases or browsing history, or an e-commerce site might recommend products based on past behavior. By delivering targeted content and offers to the right customer segments, businesses can increase engagement, conversions, and customer retention. Additionally, segmentation enables more efficient resource allocation, allowing businesses to focus their efforts on high-value customers or those with the greatest potential for future growth. In essence, customer segmentation enhances the ability to deliver the right message to the right audience at the right time.

3.Market Basket Analysis
Market Basket Analysis
is a data mining technique used by retailers and marketers to understand the purchase behavior of customers by analyzing associations between different products that are frequently bought together. This technique helps businesses discover patterns and relationships in transaction data, allowing them to identify products that tend to be purchased simultaneously or in a certain order. Market Basket Analysis uses algorithms like Association Rule Mining, with the most popular being the Apriori algorithm. These algorithms generate rules, such as "If a customer buys Product A, they are likely to also buy Product B," helping businesses make data-driven decisions.
One of the key metrics in Market Basket Analysis is support, which measures how frequently an item appears in transactions, and confidence, which represents the likelihood that if a customer buys one product, they will also buy another. Another important metric is lift, which compares the likelihood of two products being purchased together against the likelihood of their individual purchases. High lift values indicate strong associations between products, making them ideal candidates for promotional bundling or cross-selling strategies. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can optimize product placements, offer discounts, and design targeted promotions that drive sales.
Market Basket Analysis has numerous applications in retail, e-commerce, and marketing. Retailers can use the insights to improve product placement in physical stores or on e-commerce websites, ensuring that frequently purchased products are placed near each other to encourage additional purchases. For example, grocery stores might place chips and salsa near each other based on analysis showing that customers often buy them together. In e-commerce, the technique is widely used for recommendation engines, helping businesses suggest complementary products to customers during the shopping process, leading to increased average order value and better customer satisfaction.

Market Basket Analysis
is a data mining technique used by retailers and marketers to understand the purchase behavior of customers by analyzing associations between different products that are frequently bought together. This technique helps businesses discover patterns and relationships in transaction data, allowing them to identify products that tend to be purchased simultaneously or in a certain order. Market Basket Analysis uses algorithms like Association Rule Mining, with the most popular being the Apriori algorithm. These algorithms generate rules, such as "If a customer buys Product A, they are likely to also buy Product B," helping businesses make data-driven decisions.
One of the key metrics in Market Basket Analysis is support, which measures how frequently an item appears in transactions, and confidence, which represents the likelihood that if a customer buys one product, they will also buy another. Another important metric is lift, which compares the likelihood of two products being purchased together against the likelihood of their individual purchases. High lift values indicate strong associations between products, making them ideal candidates for promotional bundling or cross-selling strategies. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can optimize product placements, offer discounts, and design targeted promotions that drive sales.
Market Basket Analysis has numerous applications in retail, e-commerce, and marketing. Retailers can use the insights to improve product placement in physical stores or on e-commerce websites, ensuring that frequently purchased products are placed near each other to encourage additional purchases. For example, grocery stores might place chips and salsa near each other based on analysis showing that customers often buy them together. In e-commerce, the technique is widely used for recommendation engines, helping businesses suggest complementary products to customers during the shopping process, leading to increased average order value and better customer satisfaction.

4.Personalization using Big Data
Personalization using Big Data
refers to the process of using large volumes of customer data to tailor products, services, and experiences to individual preferences, behaviors, and needs. By analyzing data from various sources, such as past purchases, browsing history, social media activity, and demographic information, businesses can create highly personalized experiences that engage customers on a deeper level. This personalization can take many forms, such as personalized product recommendations, targeted advertising, customized email campaigns, and dynamic website content that adjusts based on user behavior..
Big data enables personalization through advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, which can process vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future behavior. For example, e-commerce platforms like Amazon and Netflix use big data to recommend products and movies based on previous interactions, increasing the likelihood of conversion and customer satisfaction. These recommendations are continually refined through real-time data analysis, ensuring that the content remains relevant to the user’s current interests. By leveraging big data, businesses can deliver highly targeted, contextually relevant content to customers at the right time, driving engagement and enhancing the overall customer experience.
Furthermore, personalization using big data extends beyond product recommendations to improve customer service and retention. For example, brands can use customer data to offer tailored discounts, personalized loyalty programs, or individualized promotions based on purchasing patterns or engagement history. Additionally, big data allows companies to create personalized marketing messages that resonate more effectively with different customer segments. By fostering a sense of personalized attention, businesses can enhance customer loyalty, increase retention rates, and ultimately drive higher lifetime value from each customer. In competitive industries, leveraging big data for personalization is a powerful way to differentiate from competitors and maintain strong, lasting customer relationships.

5.Fraud Detection
Fraud Detection
using big data refers to the process of identifying and preventing fraudulent activities by analyzing large volumes of transaction and behavior data to detect patterns that may indicate fraud. This technique is widely used in industries such as banking, insurance, e-commerce, and telecommunications, where fraudulent activities like identity theft, financial fraud, and transaction manipulation can cause significant losses. By leveraging advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time monitoring, businesses can spot irregularities and take proactive measures to mitigate fraud risks before they escalate.
Big data enables real-time fraud detection by analyzing various data points, such as transaction amounts, locations, device information, and behavioral patterns. Machine learning algorithms are particularly effective in fraud detection because they can learn from historical data and recognize subtle patterns of fraudulent behavior that might be missed by traditional rule-based systems. For example, credit card companies use big data to flag potentially fraudulent transactions by comparing them against normal spending patterns. If a transaction deviates significantly from a user's typical behavior—such as a large purchase in a foreign country—the system can trigger an alert or temporarily block the transaction. The ability to detect fraud in real-time is critical for preventing significant financial losses and protecting customer trust.
In addition to transactional data, big data also incorporates social media and geolocation data, allowing companies to enhance fraud detection systems further. For instance, analyzing users' social interactions or patterns of online activity can help identify suspicious behavior, such as accounts being accessed from unusual locations or devices. As fraudsters become more sophisticated in their methods, big data analytics can continuously adapt and refine the detection models to stay one step ahead. With the integration of big data, organizations can not only detect fraud more efficiently but also reduce false positives, ensuring legitimate transactions are processed without unnecessary delays.

6.Supply Chain Optimization
Supply Chain Optimization
using big data involves the use of advanced analytics to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain by analyzing vast amounts of data from various sources, such as suppliers, distributors, customers, and logistics operations. By processing and analyzing this data, companies can identify inefficiencies, forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Big data provides a comprehensive view of the supply chain, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize every aspect of the supply chain, from procurement to delivery.
One of the key applications of big data in supply chain optimization is demand forecasting. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, seasonality, and external factors like weather or economic conditions, companies can predict future demand more accurately. This helps businesses ensure they have the right amount of inventory at the right time, preventing stockouts or overstock situations. Big data also aids in inventory management, where real-time tracking of inventory levels, shipments, and warehouse activities can be used to optimize storage space, minimize holding costs, and reduce the risk of stock obsolescence.
OAdditionally, big data analytics can enhance logistics and transportation management. By tracking shipments in real time, companies can optimize delivery routes, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize delays. This is particularly valuable in industries like retail and manufacturing, where timely delivery is crucial. Big data also allows businesses to assess the performance of suppliers and distributors, helping them identify the most reliable partners and reduce lead times. By integrating data from various sources, businesses can build more resilient supply chains, quickly adapt to disruptions (e.g., natural disasters or political events), and ensure smoother operations overall. As a result, supply chain optimization with big data leads to cost savings, improved efficiency, and better service levels for customers.
7.Dynamic Pricing Models
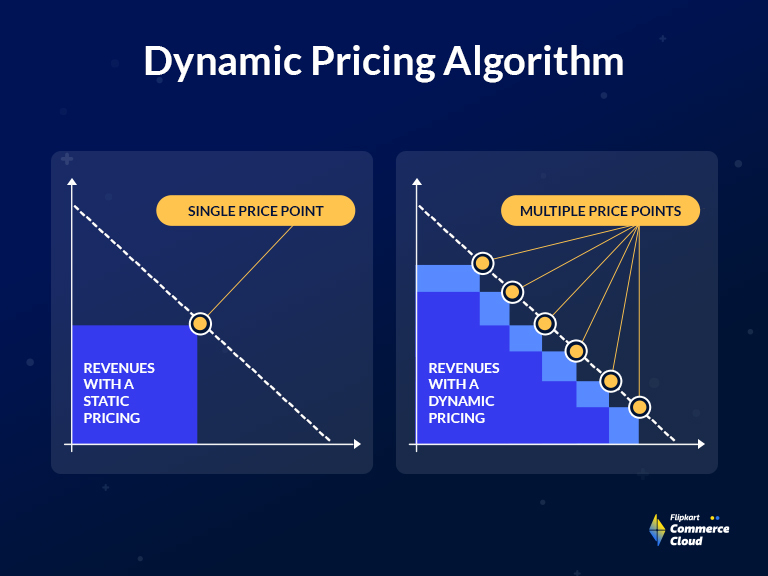
Dynamic Pricing Models
strategies where the price of a product or service is adjusted in real-time or over a period based on various factors like demand, supply, customer behavior, competitor pricing, and market conditions. This model allows businesses to optimize their pricing strategies by leveraging big data and advanced analytics. For example, e-commerce platforms, airlines, and ride-sharing services use dynamic pricing to increase revenue by adjusting prices based on real-time data, such as fluctuations in demand or the time of day. The aim is to maximize profits while staying competitive and providing customers with fair prices based on their willingness to pay.
Big data plays a crucial role in dynamic pricing by providing insights from multiple data sources. Businesses can track and analyze customer behavior, historical purchasing data, market trends, competitor prices, and other variables such as weather conditions or social events. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, companies can forecast demand patterns and adjust prices accordingly. For instance, during peak times or special events, businesses can increase prices to reflect high demand, while during off-peak periods, they can lower prices to attract more customers. This pricing flexibility helps businesses optimize their revenue streams while maintaining customer satisfaction.
A major advantage of dynamic pricing is its ability to personalize prices for different customer segments. For example, an online retailer might offer personalized discounts to loyal customers based on their past purchasing behavior, or a hotel might adjust room rates based on a guest's booking history and preferences. Moreover, dynamic pricing can also help businesses manage inventory more efficiently by adjusting prices to ensure products are sold at the right time. In industries such as retail, travel, and entertainment, dynamic pricing allows businesses to stay competitive, increase market share, and deliver more value to both customers and the company. However, implementing dynamic pricing requires careful consideration of customer perception and potential backlash, ensuring that prices remain transparent and fair to avoid customer dissatisfaction.
8.Customer Sentiment Prediction
Customer Sentiment Prediction is the process of analyzing customer feedback, reviews, social media posts, and other forms of customer communication to understand their feelings, opinions, and attitudes towards a brand, product, or service. Using big data analytics and natural language processing (NLP), businesses can predict how customers feel about their offerings and anticipate changes in customer satisfaction. This allows companies to make data-driven decisions to improve their products, services, and customer experiences. By leveraging sentiment analysis, businesses can identify positive, negative, or neutral sentiments and take appropriate actions to address customer concerns or enhance positive experiences.
The role of big data in customer sentiment prediction is vital because it enables businesses to process and analyze large volumes of unstructured data from multiple sources in real-time. Social media platforms, customer reviews, surveys, and chat interactions are rich sources of sentiment data. Big data tools, such as machine learning algorithms and NLP models, can analyze this data to identify patterns and trends in customer opinions. For instance, if a significant number of customers express dissatisfaction with a particular feature of a product, a company can quickly identify the issue and take corrective action. Sentiment prediction can also help businesses track changes in customer attitudes over time, enabling them to anticipate and respond to shifts in sentiment before they impact sales or brand reputation.
Moreover, customer sentiment prediction enables personalized marketing strategies by understanding customer preferences and emotions. By analyzing sentiment data, companies can tailor their marketing messages, advertisements, and promotional offers to resonate more deeply with specific customer segments. For example, if sentiment analysis reveals that a segment of customers feels excited about a new product launch, businesses can amplify this enthusiasm through targeted campaigns. Additionally, businesses can use sentiment insights to refine customer service strategies, ensuring that negative feedback is addressed promptly, and positive experiences are leveraged to build customer loyalty. Ultimately, sentiment prediction using big data helps companies stay ahead of customer expectations, improve customer satisfaction, and foster long-term relationships with their audience.

Customer Sentiment Prediction is the process of analyzing customer feedback, reviews, social media posts, and other forms of customer communication to understand their feelings, opinions, and attitudes towards a brand, product, or service. Using big data analytics and natural language processing (NLP), businesses can predict how customers feel about their offerings and anticipate changes in customer satisfaction. This allows companies to make data-driven decisions to improve their products, services, and customer experiences. By leveraging sentiment analysis, businesses can identify positive, negative, or neutral sentiments and take appropriate actions to address customer concerns or enhance positive experiences.
The role of big data in customer sentiment prediction is vital because it enables businesses to process and analyze large volumes of unstructured data from multiple sources in real-time. Social media platforms, customer reviews, surveys, and chat interactions are rich sources of sentiment data. Big data tools, such as machine learning algorithms and NLP models, can analyze this data to identify patterns and trends in customer opinions. For instance, if a significant number of customers express dissatisfaction with a particular feature of a product, a company can quickly identify the issue and take corrective action. Sentiment prediction can also help businesses track changes in customer attitudes over time, enabling them to anticipate and respond to shifts in sentiment before they impact sales or brand reputation.
Moreover, customer sentiment prediction enables personalized marketing strategies by understanding customer preferences and emotions. By analyzing sentiment data, companies can tailor their marketing messages, advertisements, and promotional offers to resonate more deeply with specific customer segments. For example, if sentiment analysis reveals that a segment of customers feels excited about a new product launch, businesses can amplify this enthusiasm through targeted campaigns. Additionally, businesses can use sentiment insights to refine customer service strategies, ensuring that negative feedback is addressed promptly, and positive experiences are leveraged to build customer loyalty. Ultimately, sentiment prediction using big data helps companies stay ahead of customer expectations, improve customer satisfaction, and foster long-term relationships with their audience.

Comments