AR & VR in Healthcare
1. what is AR & VR in Healthcare?

AR & VR in Healthcarein Healthcare are transformative technologies that are revolutionizing the medical field by providing innovative ways to diagnose, treat, and manage various health conditions. Both technologies enhance patient care, assist medical professionals in training, and offer immersive treatment experiences. AR and VR can be used to visualize complex medical data, simulate surgeries, or provide therapeutic environments, making them invaluable tools for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Augmented Reality (AR) in healthcare overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the doctor’s view with valuable data, medical images, or annotations in real-time. Surgeons, for instance, can use AR glasses or heads-up displays during procedures to access patient information, such as X-rays or MRI scans, while performing surgery. This allows for more precise operations without needing to look away from the patient. AR is also used in medical education and training, where students can view 3D models of human anatomy and interact with them for a better understanding of how organs and systems function. Additionally, AR applications help patients with rehabilitation by providing interactive, gamified therapy sessions, encouraging movement and progress through visual cues and feedback.
On the other hand, Virtual Reality (VR) creates an entirely immersive environment, providing medical professionals and patients with experiences that simulate various medical situations. In medical training, VR allows students and professionals to practice complex surgeries, patient interactions, or diagnostic procedures in a risk-free, controlled environment. For example, VR simulators can recreate realistic surgical scenarios where students can hone their skills before performing actual operations. Similarly, VR is increasingly being used in mental health treatment; for example, VR therapy is used to treat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, or phobias by immersing patients in virtual environments where they can face their fears in a controlled and safe space. This form of exposure therapy has been shown to help patients confront their issues gradually and reduce their symptoms.
2.Virtual Surgery Simulations
Virtual Surgery Simulations
are computer-generated environments that allow medical professionals to practice and refine their surgical skills in a safe, risk-free setting. These simulations utilize Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies to create highly detailed, interactive, and realistic virtual surgeries, enabling surgeons, medical students, and other healthcare practitioners to gain experience without performing actual procedures on real patients. The goal is to improve surgical proficiency, reduce errors, and enhance training and education in the medical field.
One of the main benefits of virtual surgery simulations is the ability to simulate complex and rare surgical procedures that might not often occur in a medical professional’s career. This gives practitioners the opportunity to familiarize themselves with various scenarios, tools, and techniques in advance, making them more prepared when handling real-life situations. In these simulations, the user can interact with a virtual 3D model of a patient’s body, using controllers or gloves to perform procedures such as incision, suturing, or organ repair. The simulation can provide real-time feedback on the user's actions, tracking their movements, precision, and speed, which helps to improve their technique and decision-making abilities.
Virtual surgery simulators also support the learning curve for novice surgeons by allowing them to practice basic skills like handling surgical instruments, making incisions, or stitching wounds. For more experienced surgeons, these simulations allow for honing specialized skills, such as performing minimally invasive surgeries with precision and control. Surgeons can practice using advanced technologies like robotic surgical systems or explore different approaches to a procedure, all in a controlled, risk-free environment. This kind of training helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application, ultimately leading to improved patient safety and surgical outcomes.
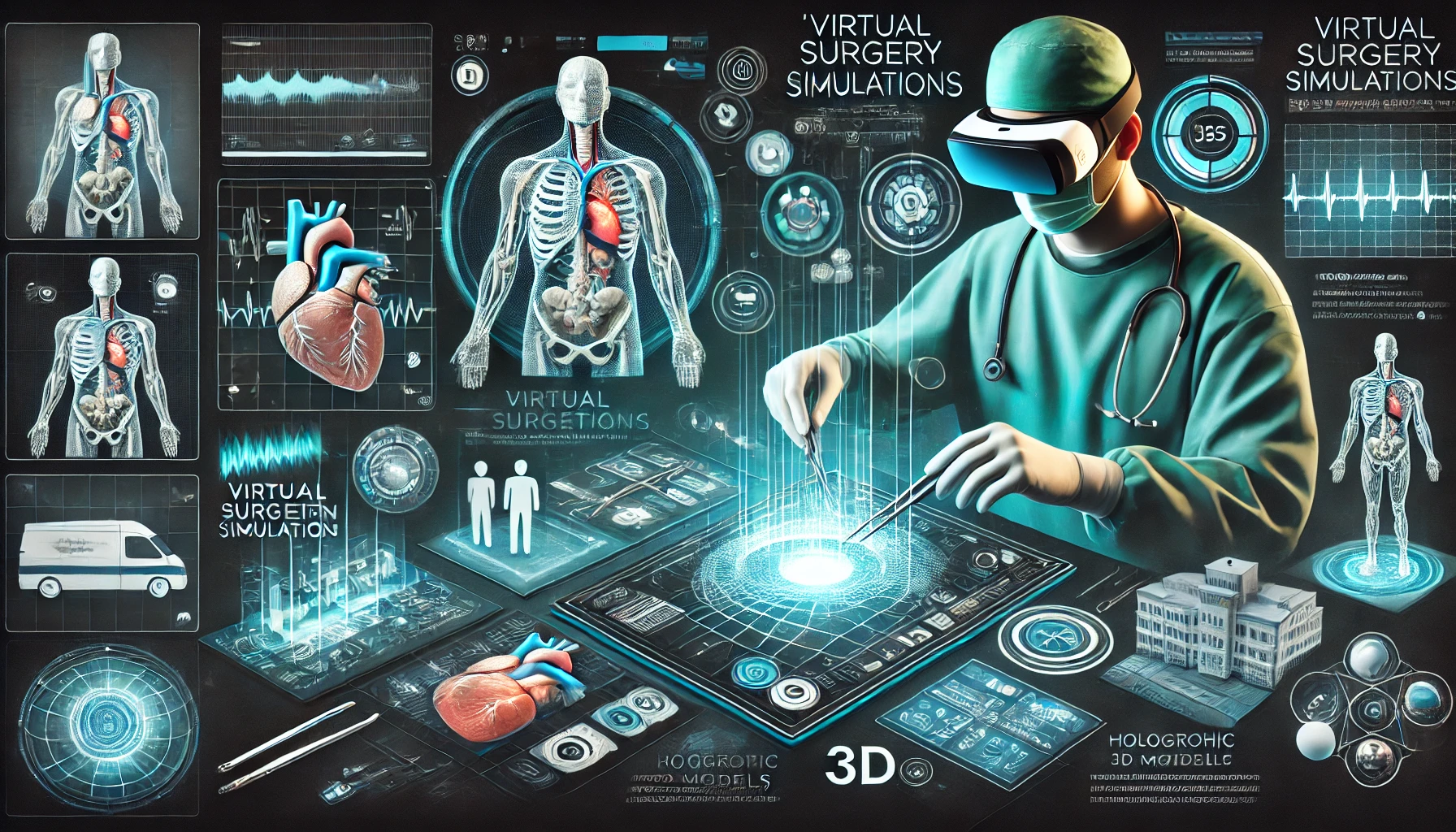

3.AR for Medical Training
AR for Medical Training
is a powerful technology that enhances the way medical professionals and students learn by integrating digital information with the real-world environment. Through the use of AR devices, such as smart glasses or AR applications on smartphones and tablets, medical students and healthcare professionals can overlay detailed digital content, like 3D anatomical models, medical images, and procedural guidance, on top of physical objects and environments. This hands-on approach enables learners to better visualize, understand, and interact with complex medical concepts and procedures.
One of the key advantages of AR in medical training is the ability to create interactive 3D models of human anatomy. Students can explore organs, tissues, and systems in a detailed, 360-degree view, allowing them to study their structure, function, and interactions. Unlike traditional textbooks or 2D diagrams, AR provides an immersive, lifelike experience, making it easier for learners to grasp complex subjects like human anatomy, physiology, and pathology. For example, students can virtually dissect organs or perform simulated surgeries, gaining practical experience without the need for cadavers or live patients. This ability to interact with digital models greatly improves retention and comprehension, especially in fields that require spatial understanding and precision.
Additionally, AR in medical training can be used for real-time guidance during actual clinical practice. For example, AR glasses or headsets can provide step-by-step instructions during surgical procedures, showing the surgeon real-time data, such as patient vitals or images from diagnostic tools, while also offering a visual overlay of the surgery's key steps. This not only helps new practitioners learn the procedure more efficiently but also aids experienced surgeons by minimizing the need for traditional references, ensuring they focus solely on the patient. Furthermore, AR-based simulations allow learners to practice procedures in a safe, risk-free environment, where they can make mistakes and correct them without any consequences, fostering confidence and expertise before performing on actual patients.
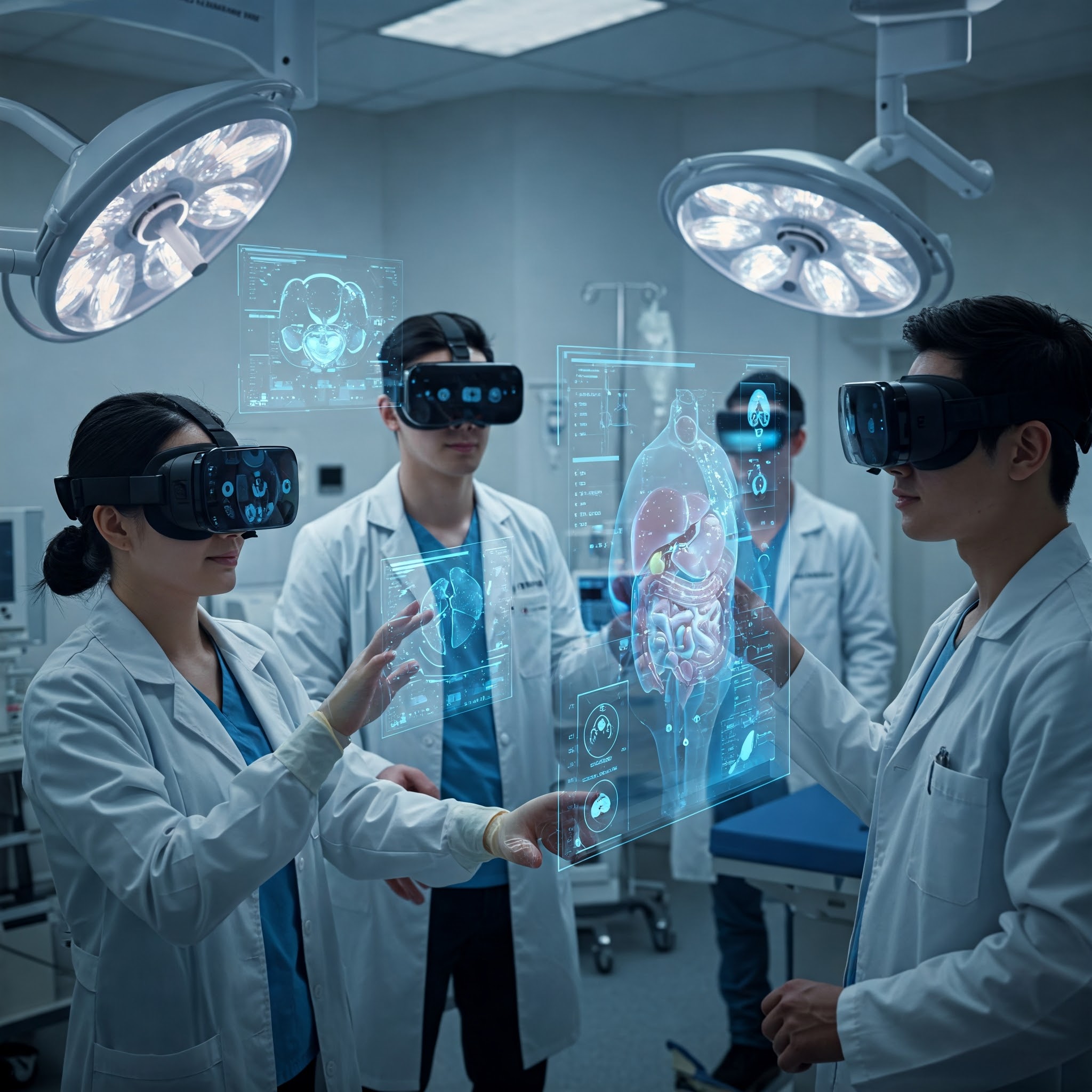

AR for Medical Training
is a powerful technology that enhances the way medical professionals and students learn by integrating digital information with the real-world environment. Through the use of AR devices, such as smart glasses or AR applications on smartphones and tablets, medical students and healthcare professionals can overlay detailed digital content, like 3D anatomical models, medical images, and procedural guidance, on top of physical objects and environments. This hands-on approach enables learners to better visualize, understand, and interact with complex medical concepts and procedures.
One of the key advantages of AR in medical training is the ability to create interactive 3D models of human anatomy. Students can explore organs, tissues, and systems in a detailed, 360-degree view, allowing them to study their structure, function, and interactions. Unlike traditional textbooks or 2D diagrams, AR provides an immersive, lifelike experience, making it easier for learners to grasp complex subjects like human anatomy, physiology, and pathology. For example, students can virtually dissect organs or perform simulated surgeries, gaining practical experience without the need for cadavers or live patients. This ability to interact with digital models greatly improves retention and comprehension, especially in fields that require spatial understanding and precision.
Additionally, AR in medical training can be used for real-time guidance during actual clinical practice. For example, AR glasses or headsets can provide step-by-step instructions during surgical procedures, showing the surgeon real-time data, such as patient vitals or images from diagnostic tools, while also offering a visual overlay of the surgery's key steps. This not only helps new practitioners learn the procedure more efficiently but also aids experienced surgeons by minimizing the need for traditional references, ensuring they focus solely on the patient. Furthermore, AR-based simulations allow learners to practice procedures in a safe, risk-free environment, where they can make mistakes and correct them without any consequences, fostering confidence and expertise before performing on actual patients.

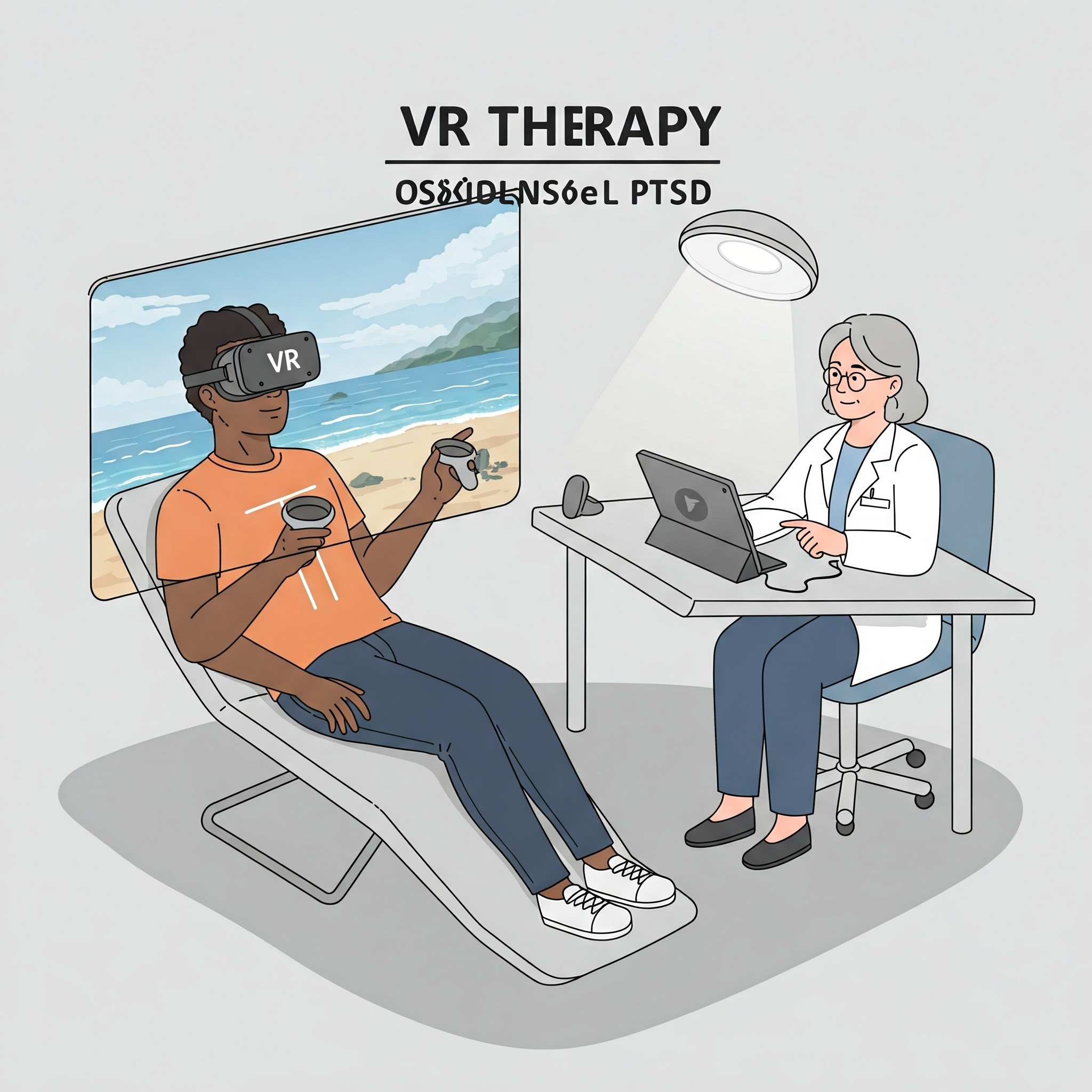
4.VR Therapy for PTSD
VR Therapy for PTSD
is an innovative and effective treatment approach that uses Virtual Reality (VR) technology to help patients confront and process traumatic memories in a controlled and safe environment. PTSD is a mental health condition triggered by experiencing or witnessing traumatic events, leading to symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and emotional numbness. Traditional therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or exposure therapy, are commonly used to treat PTSD. However, VR therapy offers a unique and immersive approach that can significantly enhance the healing process.
In VR therapy for PTSD, patients are exposed to simulated environments that replicate situations or scenarios related to their trauma. These virtual environments are carefully designed to be as realistic as possible, allowing patients to safely experience and process their emotions related to the trauma without the risks of real-life exposure. The VR system typically includes a headset and motion controllers, which create an immersive experience where patients can interact with the virtual world. For example, a war veteran might be guided through a virtual combat scenario, allowing them to confront their past trauma under the supervision of a trained therapist. The therapist can adjust the intensity of the virtual experience, gradually increasing the difficulty level as the patient becomes more comfortable and begins to process the traumatic memories.
The core principle behind VR therapy for PTSD is exposure therapy, which involves helping patients gradually face their fears or traumatic memories in a safe, controlled setting. By allowing patients to experience trauma-related scenarios in VR, they can work through their emotional responses, reduce avoidance behaviors, and decrease the emotional impact of the trauma. The immersive nature of VR can make the experience more effective than traditional methods, as it engages the patient’s senses and creates a stronger sense of presence in the therapeutic environment. VR therapy also allows for customization based on the patient’s specific trauma, making it a highly personalized form of treatment.
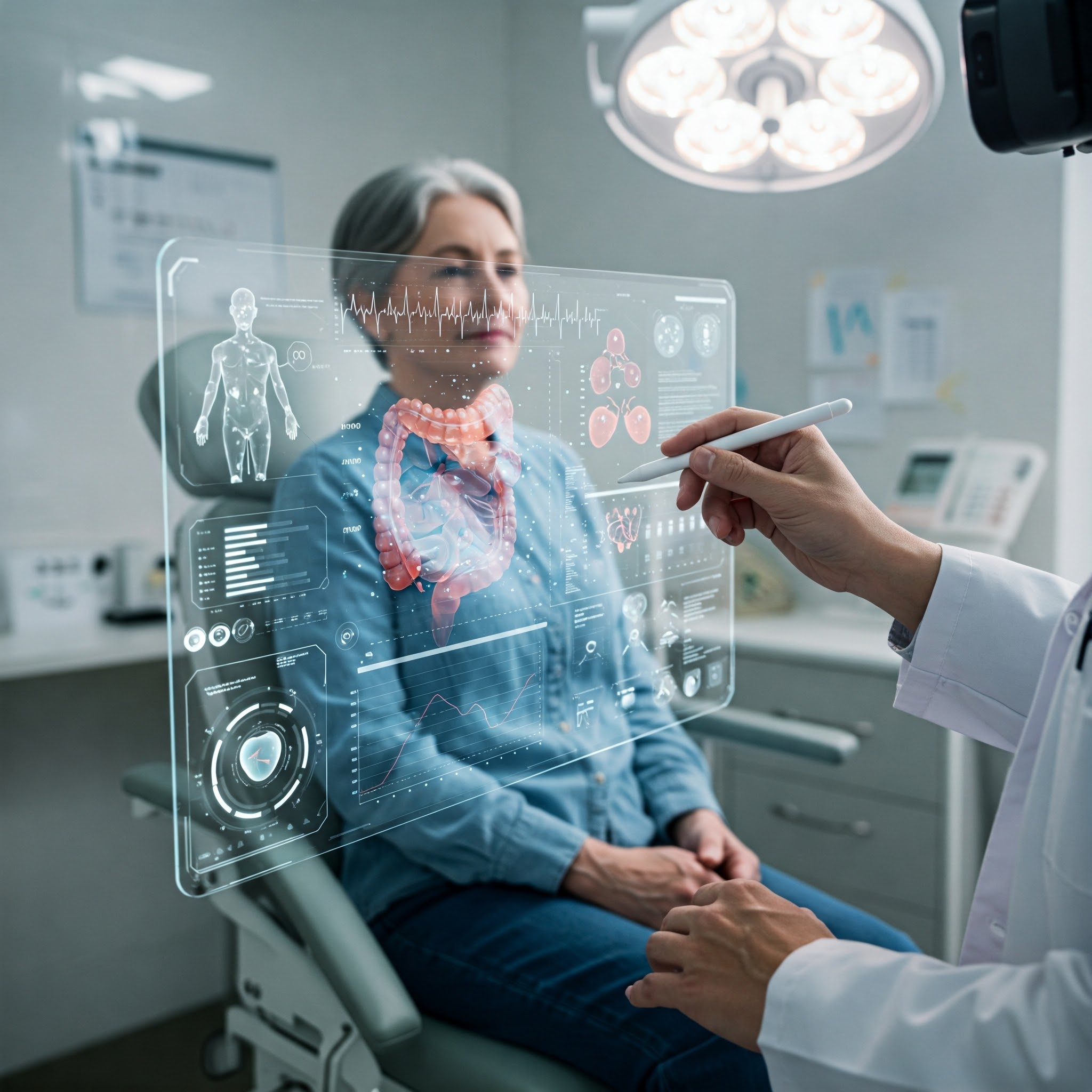
5.AR in Patient Diagnosis
AR in Patient Diagnosis
is revolutionizing the way healthcare professionals examine, diagnose, and treat patients by enhancing their ability to visualize and analyze medical data in real time. Using AR technology, doctors can overlay digital information such as medical imaging, test results, and patient data directly onto the patient’s body or diagnostic equipment. This allows for more accurate and efficient diagnoses by providing clinicians with a richer, more interactive understanding of a patient’s condition, all while maintaining their focus on the patient without needing to shift attention away to look at separate screens or physical documents.
For example, AR can enhance radiology and imaging diagnostics by displaying 3D models of a patient’s organs or internal structures, such as bones, muscles, or tumors, overlaid onto the patient's body. With the help of AR glasses or smart devices, a doctor can visualize X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs as 3D holograms that interact with the patient in real-time, helping them understand the spatial relationships between organs and structures better. This 3D visualization improves the precision of diagnosing conditions like tumors, fractures, or vascular issues, which might be harder to detect using traditional 2D scans alone. Surgeons, for example, can view a patient’s exact anatomy, identifying areas of concern without needing to reference external sources or imaging, streamlining both the diagnosis and treatment planning process.
AR also plays a significant role in pre-surgical planning and guiding doctors during complex procedures. Surgeons can use AR to simulate surgery on a 3D representation of a patient's body before the actual procedure, helping them plan the most effective approach and minimize potential risks. By overlaying patient-specific anatomical data onto the surgical field, AR can provide real-time guidance during surgery, ensuring that doctors make the most precise incisions and decisions based on the patient's unique internal structure. This enhances patient safety and reduces errors during surgery, ultimately improving clinical outcomes.
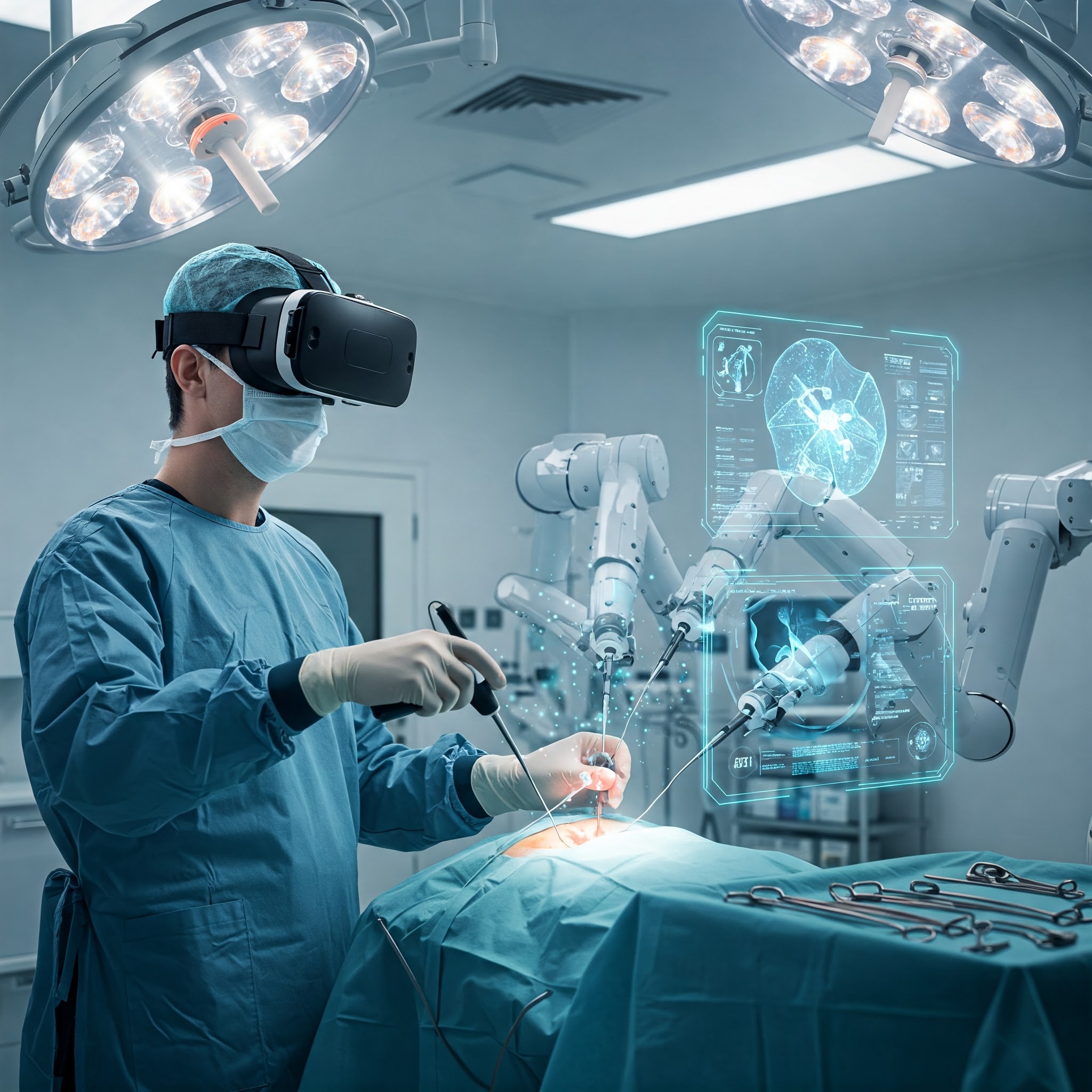
6.Remote Surgery Using VR
Remote Surgery Using VR
is an advanced and groundbreaking concept that allows surgeons to perform surgical procedures on patients who may be located far away, utilizing virtual reality and other technologies to control robotic surgical instruments in real time. This innovative approach addresses challenges such as geographical limitations, a shortage of specialized surgeons in certain areas, and the need for highly precise, complex surgeries that require expert intervention. By combining VR, robotic surgery, and telecommunication systems, remote surgery can be performed safely and effectively with minimal delay, offering patients access to the best healthcare professionals regardless of their location.
In remote surgery using VR, the surgeon operates in a VR-controlled environment where they use haptic feedback-enabled controllers or robotic arms to manipulate surgical instruments, allowing them to interact with the patient’s body in a detailed and precise manner. The VR setup includes a real-time video feed from cameras placed on the patient, offering a 360-degree view of the surgical site. This allows the surgeon to immerse themselves in the procedure as if they were physically present in the operating room. High-definition 3D imaging provides a clear and accurate representation of the patient's anatomy, which is essential for performing delicate surgeries, such as neurosurgeries or cardiac procedures.
The use of haptic feedback in VR systems adds another dimension to remote surgery, providing the surgeon with tactile sensations that mimic the physical feedback they would experience during actual surgery. This helps ensure that they can perform tasks like cutting, suturing, or manipulating tissues with the necessary precision and confidence. Since the surgeon is working remotely, there is typically a team of medical professionals on-site, assisting with patient positioning, prepping, and monitoring. The surgeon's commands are transmitted to the robotic system via a low-latency network, ensuring that movements and actions are executed instantly with minimal delay, which is crucial for maintaining safety during surgery.
7.AR for Prosthetic Assistance
AR for Prosthetic Assistance
s an innovative approach that leverages Augmented Reality (AR) technology to improve the functionality, design, and user experience of prosthetic devices. By combining digital overlays with real-world environments, AR helps individuals with prosthetics gain better control, comfort, and mobility, while also enhancing the design and fit of prosthetic limbs. This technology allows for real-time visualization, adjustments, and interaction with prosthetic devices, making them more personalized and adaptive to the user's needs. It also enables the integration of additional features that enhance the overall functionality of the prosthetic, leading to a more natural and intuitive experience for the user.
One of the most significant benefits of AR for prosthetic assistance is its ability to provide real-time feedback during the fitting and customization process. By using AR glasses or smartphones, a prosthetist can visualize the user's anatomy, measure the fit of the prosthetic, and simulate how different adjustments would affect the device’s performance. For example, the prosthetist could overlay 3D models of the prosthetic onto the user's residual limb to ensure a precise fit and alignment. This visualization helps identify potential issues like pressure points or improper alignment before the prosthetic is manufactured or fitted, leading to a more comfortable and functional device. Furthermore, users themselves can interact with the AR system to try out different prosthetic components or features, like joints, fingers, or foot designs, to determine what works best for their specific needs.
AR technology also plays a crucial role in enhancing user training and improving the overall experience of prosthetic users. For individuals who are new to using prosthetics, AR can offer interactive guidance on how to properly wear, adjust, and use the device. For example, users can receive real-time visual instructions, such as how to align their limb with the prosthetic or how to adjust settings for different activities (walking, running, etc.). These instructions can be overlaid directly onto the user's view of the prosthetic or their environment, making it easier for them to understand and perform the necessary actions. Moreover, AR-based training apps can help users practice movements and activities with their prosthetic in a safe, controlled manner, allowing them to gradually build strength, confidence, and coordination.
8.VR in Mental Health Therapy
VR in Mental Health Therapy is an emerging and innovative treatment approach that uses immersive virtual environments to help individuals manage and treat various mental health conditions. By creating a simulated, controlled space, VR therapy allows patients to engage in therapeutic experiences that can be customized to address specific issues such as anxiety, PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder), depression, phobias, and stress management. The immersive nature of VR enables individuals to confront and process emotions, memories, and behaviors in a way that traditional therapies might not be able to provide, offering a unique opportunity for healing and growth.
One of the most notable applications of VR in mental health therapy is its use in exposure therapy, particularly for conditions like phobias and PTSD. In traditional exposure therapy, patients are gradually exposed to the object or situation they fear in a safe and controlled environment. VR enhances this process by offering virtual simulations where patients can confront their fears or traumatic memories in a safe, controlled, and repeatable way. For instance, a person with a fear of flying can experience a virtual flight to help desensitize them to the triggers associated with air travel. Similarly, individuals with PTSD can use VR to safely revisit and process traumatic experiences with the guidance of a therapist, helping them reduce the emotional intensity of their memories over time..
VR therapy also enables mindfulness and relaxation techniques, offering patients virtual environments designed to promote calmness and stress reduction. By immersing patients in serene, nature-inspired landscapes or peaceful settings, VR can guide individuals through meditation or breathing exercises, helping them manage anxiety, stress, or depression. The sense of presence that VR provides—feeling "there" in the virtual world—can significantly enhance the effectiveness of these therapeutic interventions, as patients can feel more immersed in the relaxation experience. This can be especially beneficial for individuals who struggle with anxiety in traditional therapy sessions or those who find it difficult to relax in real-world environments.

VR in Mental Health Therapy is an emerging and innovative treatment approach that uses immersive virtual environments to help individuals manage and treat various mental health conditions. By creating a simulated, controlled space, VR therapy allows patients to engage in therapeutic experiences that can be customized to address specific issues such as anxiety, PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder), depression, phobias, and stress management. The immersive nature of VR enables individuals to confront and process emotions, memories, and behaviors in a way that traditional therapies might not be able to provide, offering a unique opportunity for healing and growth.
One of the most notable applications of VR in mental health therapy is its use in exposure therapy, particularly for conditions like phobias and PTSD. In traditional exposure therapy, patients are gradually exposed to the object or situation they fear in a safe and controlled environment. VR enhances this process by offering virtual simulations where patients can confront their fears or traumatic memories in a safe, controlled, and repeatable way. For instance, a person with a fear of flying can experience a virtual flight to help desensitize them to the triggers associated with air travel. Similarly, individuals with PTSD can use VR to safely revisit and process traumatic experiences with the guidance of a therapist, helping them reduce the emotional intensity of their memories over time..
VR therapy also enables mindfulness and relaxation techniques, offering patients virtual environments designed to promote calmness and stress reduction. By immersing patients in serene, nature-inspired landscapes or peaceful settings, VR can guide individuals through meditation or breathing exercises, helping them manage anxiety, stress, or depression. The sense of presence that VR provides—feeling "there" in the virtual world—can significantly enhance the effectiveness of these therapeutic interventions, as patients can feel more immersed in the relaxation experience. This can be especially beneficial for individuals who struggle with anxiety in traditional therapy sessions or those who find it difficult to relax in real-world environments.

Comments