AI in Robotics
1. What is AI in Robotics ?
AI in Robotics refers to the integration of artificial intelligence techniques into robotic systems, enabling them to perceive, learn, adapt, and make decisions autonomously. Unlike traditional robots that follow pre-programmed instructions, AI-powered robots use machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing to interact with their environment intelligently. These robots can recognize objects, navigate spaces, and even understand human speech, making them highly useful in various industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. Autonomous robots, such as self-driving cars and warehouse robots, rely on AI algorithms to analyze sensor data, detect obstacles, and make real-time decisions.
AI-powered robots are revolutionizing fields like healthcare, defense, and service industries. In medicine, robotic surgeons assist in performing minimally invasive surgeries with high precision. In the military, autonomous drones carry out reconnaissance missions, reducing risks for soldiers. AI-driven service robots, such as chatbots and humanoid assistants, are enhancing customer interactions in retail and hospitality. However, challenges like high development costs, ethical concerns, and safety risks must be addressed to ensure responsible AI integration in robotics. As technology advances, AI-driven robots are expected to become smarter, more autonomous, and seamlessly integrated into daily life, improving efficiency and productivity across industries.
2. Autonomous Navigation
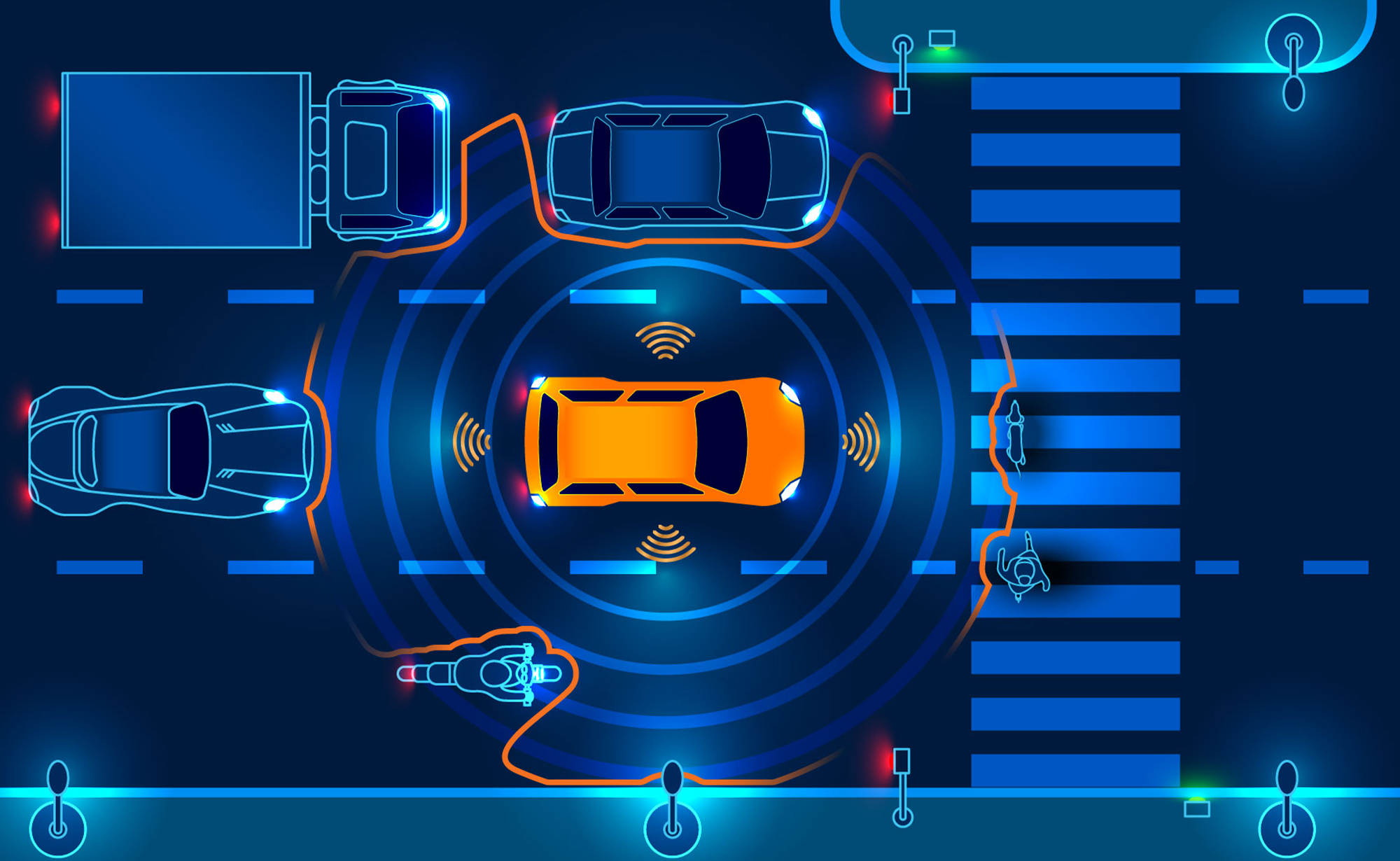
Autonomous Navigation is the ability of a robot, vehicle, or drone to move through an environment without human intervention. It relies on AI, machine learning, computer vision, and sensor data to detect obstacles, plan routes, and make real-time decisions. This technology is widely used in self-driving cars, drones, robotic vacuum cleaners, and warehouse robots. Sensors like LiDAR, cameras, GPS, and ultrasonic sensors help autonomous systems understand their surroundings and navigate safely. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a crucial technique that allows robots to build a map of their environment while determining their position within it
Self-driving cars from companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Uber use deep learning and reinforcement learning to analyze road conditions, recognize traffic signs, and avoid collisions. Autonomous drones assist in military surveillance, disaster relief, and agricultural monitoring by navigating complex terrains. In industrial settings, autonomous robots optimize warehouse operations by moving goods efficiently without human guidance. Despite its advancements, autonomous navigation faces challenges like weather conditions, unpredictable human behavior, and cybersecurity threats. However, ongoing AI research and improved sensor technology are making autonomous systems safer, more reliable, and widely applicable across industries.
With advancements in AI, deep learning, and edge computing, autonomous navigation systems are becoming smarter and more efficient. Real-time data processing, improved object detection, and enhanced decision-making enable self-driving vehicles and robots to operate in complex and dynamic environments. For example, autonomous delivery robots are now being tested in urban areas to transport goods without human supervision. Similarly, agricultural robots use AI-powered navigation to automate tasks like harvesting, weeding, and soil analysis.
However, several challenges remain. Unpredictable environments, sensor malfunctions, and ethical dilemmas pose risks to fully autonomous systems. For instance, self-driving cars must make split-second decisions in emergency situations, raising concerns about liability and safety regulations. Moreover, cybersecurity threats can compromise the integrity of autonomous systems, making them vulnerable to hacking. To overcome these obstacles, researchers are developing better AI models, redundancy mechanisms, and regulatory frameworks to ensure safe and responsible deployment. As technology progresses, autonomous navigation will play a crucial role in transportation, logistics, healthcare, and smart cities, transforming the way we interact with intelligent machines.
3. AI-powered Drones
AI-powered Drones are autonomous aerial systems that use artificial intelligence for navigation, object detection, and decision-making. These drones rely on computer vision, deep learning, and sensor fusion to analyze their surroundings and adapt to dynamic environments. Equipped with LiDAR, GPS, and high-resolution cameras, AI-driven drones can perform complex tasks such as surveillance, mapping, and disaster response. Their ability to self-learn and optimize flight paths makes them highly efficient in areas where manual control is challenging.
One of the most significant applications of AI-powered drones is in agriculture, where they help farmers monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and detect pest infestations. In the logistics industry, companies like Amazon and UPS are testing drone-based package delivery systems to improve efficiency. Additionally, AI drones play a crucial role in search and rescue missions, where they can quickly scan large areas, identify survivors, and relay critical information to emergency teams.
DDespite their advantages, AI-powered drones face challenges such as regulatory restrictions, privacy concerns, and limited battery life. Governments worldwide are working on air traffic management systems for drones to ensure safe integration into civilian airspace. As technology advances, AI-powered drones are expected to become more autonomous, efficient, and widely adopted across industries, revolutionizing fields like security, healthcare, and environmental conservation.

4. Industrial Robots
Industrial Robots
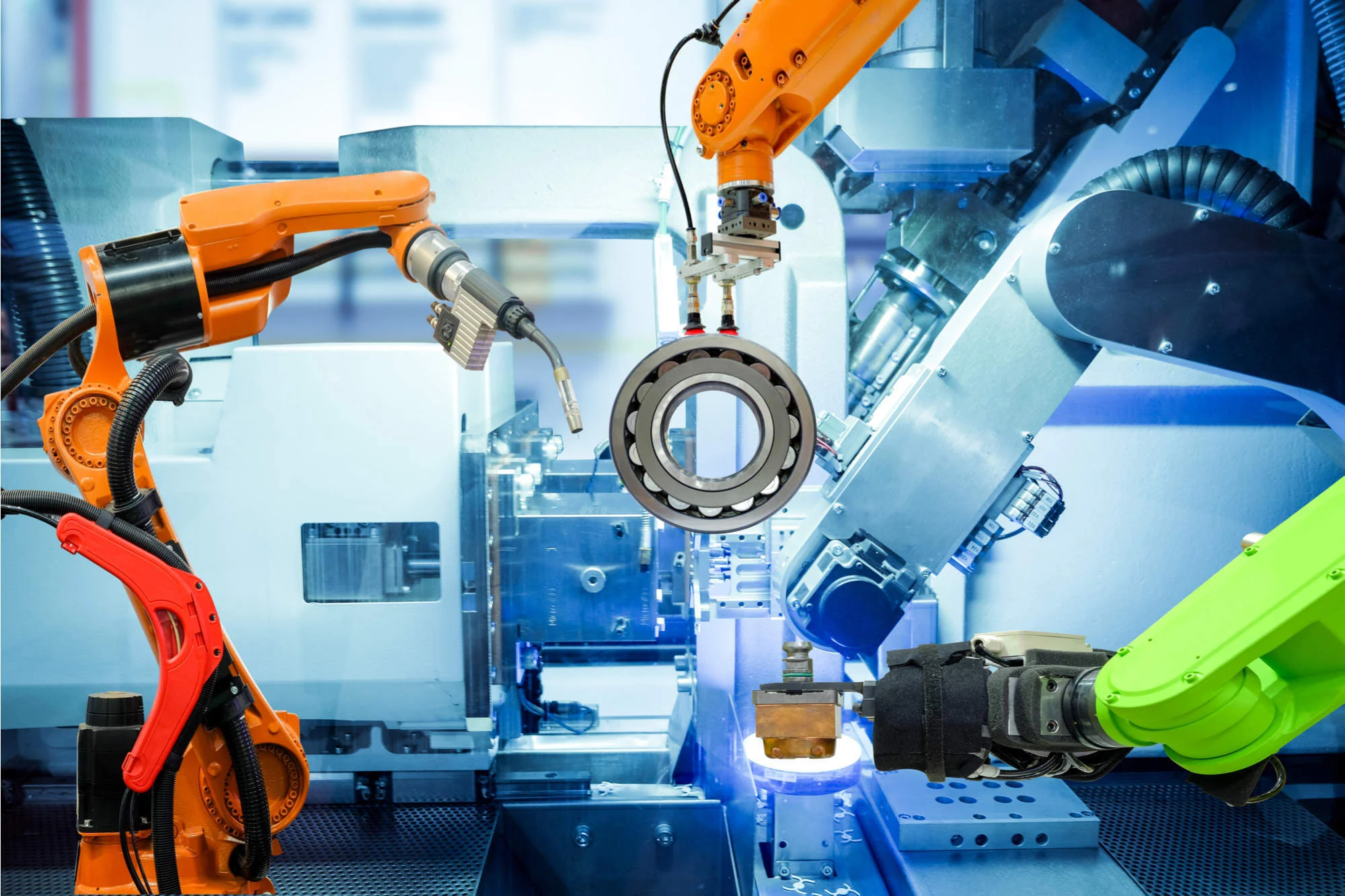
are AI-powered machines designed to perform repetitive and complex tasks in manufacturing, assembly lines, and production facilities. These robots are equipped with computer vision, machine learning, and advanced sensors to improve efficiency, precision, and automation. Unlike traditional robotic arms that follow predefined instructions, AI-driven industrial robots can adapt to changing environments, detect defects, and optimize workflows. Industries such as automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals widely use these robots to enhance productivity and reduce human labor in hazardous conditions.
AI-powered industrial robots have transformed manufacturing processes by enabling predictive maintenance, real-time quality inspection, and smart automation. For example, cobot (collaborative robot) arms work alongside human workers, increasing efficiency without compromising safety. In the automotive industry, AI robots handle welding, painting, and assembly tasks, ensuring precision and reducing waste. Additionally, AI-driven robots in warehouses, such as Amazon’s robotic systems, help streamline inventory management and order fulfillment.
Despite their advantages, AI-driven industrial robots face challenges such as high initial costs, complex integration, and workforce adaptation. Many industries require skilled technicians to operate and maintain these robots, leading to a demand for specialized training programs. However, as AI technology advances, industrial robots are expected to become more affordable, autonomous, and intelligent, enabling fully automated smart factories. With the rise of Industry 4.0, AI-driven robots will play a crucial role in reshaping global manufacturing and logistics.
5. Humanoid Robots
Humanoid Robots are AI-powered robots designed to resemble and function like humans. These robots typically have a head, torso, arms, and legs, allowing them to interact with the environment in a human-like manner. They use computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning to recognize faces, understand speech, and respond to human interactions. Examples of humanoid robots include Sophia by Hanson Robotics and ASIMO by Honda, which are capable of conversations, facial expressions, and even learning from their surroundings.
Humanoid robots are used in healthcare, customer service, education, and entertainment. In hospitals, they assist patients by providing therapy, guiding visitors, and helping elderly individuals with daily activities. In customer service, humanoid robots like Pepper interact with customers, answer queries, and provide information. These robots are also used in education to teach children languages and STEM concepts interactively. In entertainment, they perform at events, act in movies, and engage audiences with lifelike expressions and movements. .
Despite their advancements, humanoid robots face challenges such as high production costs, complex programming, and ethical concerns regarding AI-driven autonomy. Achieving natural human-like movement and emotions is still a major challenge for robotic developers. However, with continuous advancements in AI, deep learning, and robotics, humanoid robots are expected to become more intelligent, affordable, and widely used in everyday life. In the future, they may serve as companions, assistants, and even emergency responders, transforming how humans interact with machines.
6. AI in Space Exploration
AI in Space Exploration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a crucial role in space exploration, helping scientists and engineers analyze vast amounts of data, automate spacecraft operations, and assist in planetary research. AI-powered systems are used in satellites, rovers, space telescopes, and autonomous probes to enhance decision-making, navigation, and communication. NASA, ISRO, and other space agencies utilize AI for tasks such as trajectory optimization, anomaly detection, and deep-space exploration, making space missions more efficient and successful.
AI is used in various aspects of space exploration, including autonomous spacecraft navigation, robotic rovers, and data analysis. The Mars rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance use AI to navigate rough terrains, avoid obstacles, and analyze rock samples for signs of life. AI-powered satellites monitor climate change, track asteroids, and improve Earth observation. Additionally, AI helps astronauts by managing life-support systems, detecting equipment failures, and assisting in scientific experiments aboard the International Space Station (ISS)..
Despite its benefits, AI in space exploration faces challenges such as limited computational power, harsh space environments, and the need for real-time decision-making. Spacecraft must function autonomously due to communication delays with Earth, requiring highly reliable and self-learning AI systems. In the future, AI will play a major role in interstellar travel, space colonization, and deep-space mining, enabling humanity to explore distant planets and galaxies more effectively.

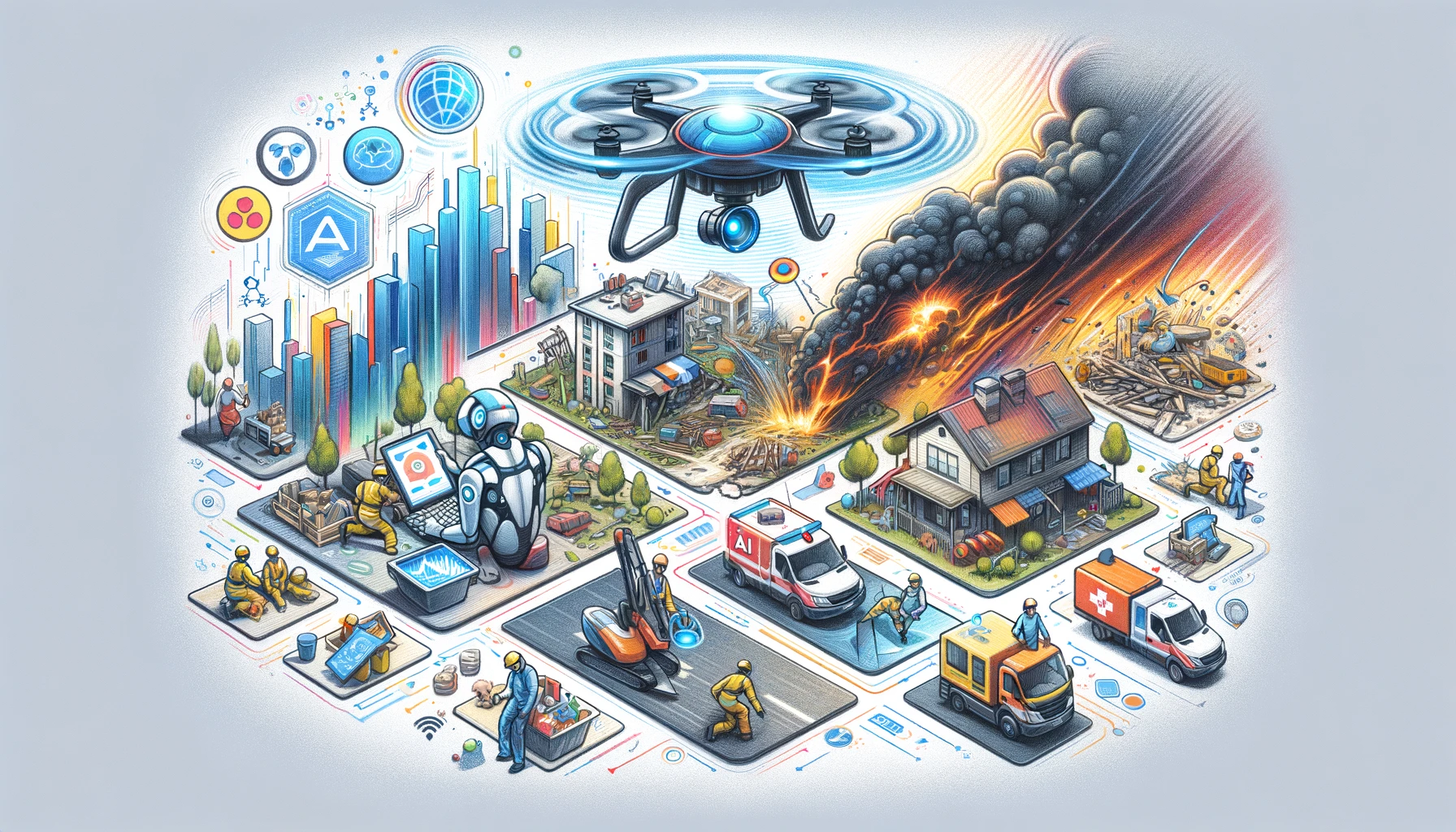
7. AI for Disaster Response
AI for Disaster Response
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming disaster response and management by enabling faster decision-making, real-time data analysis, and predictive modeling. AI-powered systems can analyze satellite images, social media data, and weather patterns to detect disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires before they escalate. Governments, emergency responders, and humanitarian organizations use AI to assess damage, allocate resources, and coordinate rescue operations more efficiently, saving lives and reducing economic losses.
MAI is widely used in early warning systems, drone surveillance, and emergency communication networks. Machine learning models predict natural disasters by analyzing historical data and real-time environmental conditions. Drones equipped with AI can survey affected areas, identify survivors, and map disaster zones for better planning. AI chatbots and automated systems help provide emergency alerts, medical assistance, and relief coordination, ensuring that affected communities receive timely support.
While AI enhances disaster response, challenges such as data accuracy, ethical concerns, and the need for robust AI models must be addressed. AI systems require high-quality real-time data to make accurate predictions and decisions. Additionally, integrating AI with existing disaster management frameworks requires proper infrastructure and collaboration among governments, NGOs, and tech companies. In the future, AI will continue to evolve with advanced robotics, deep learning, and real-time satellite monitoring, making disaster response more effective and life-saving.

8. AI-powered Prosthetics
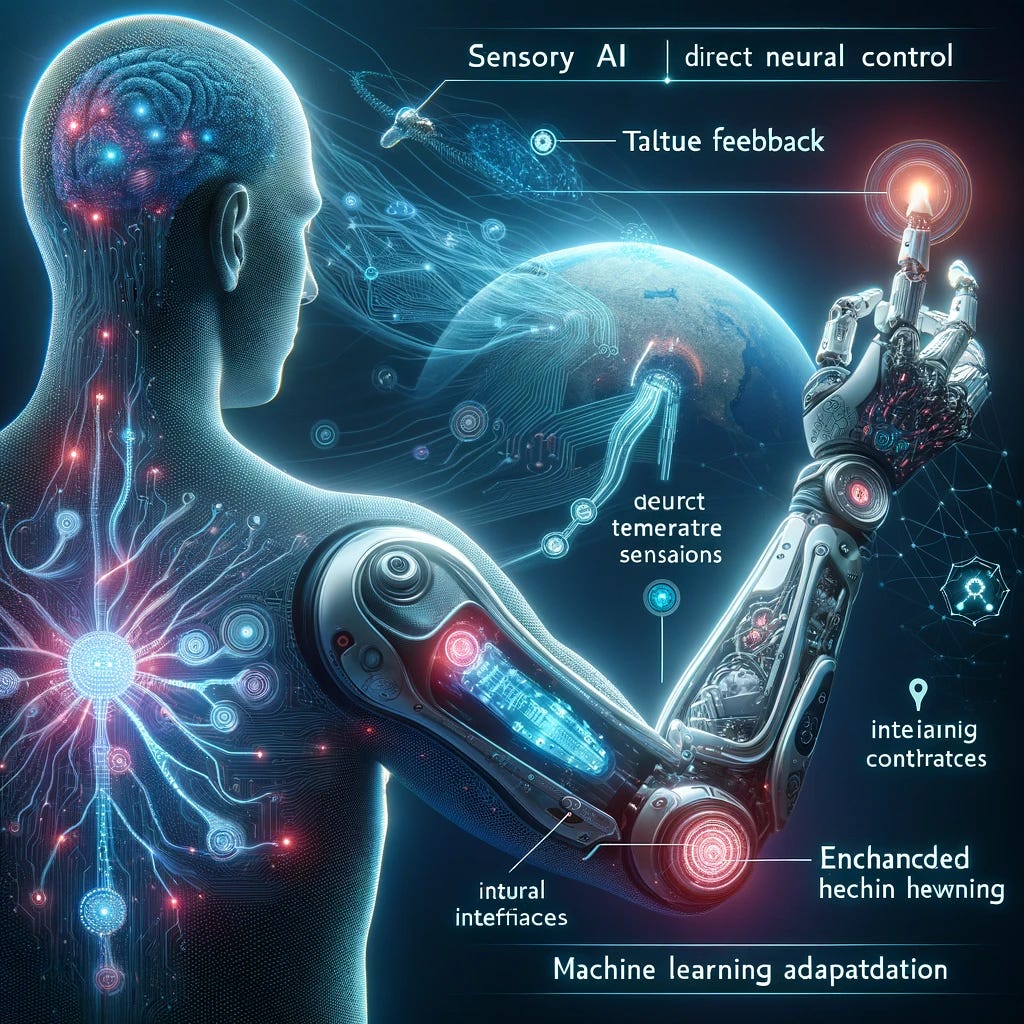
AI-powered Prosthetics are revolutionizing the field of medical technology, enabling individuals with limb loss to regain mobility and functionality. Unlike traditional prosthetics, AI-driven prosthetic limbs adapt to user movements, learn from patterns, and provide real-time adjustments for improved comfort and usability. These advanced prosthetics use machine learning algorithms, sensors, and robotics to mimic natural limb movements, allowing users to perform daily activities with greater ease.
AI-powered prosthetic limbs utilize neural interfaces, muscle sensors (EMG), and computer vision to interpret user intentions. By analyzing signals from the brain or muscles, AI algorithms predict movement patterns and adjust the prosthetic in real time. Some modern prosthetics are even equipped with haptic feedback technology, enabling users to sense touch and pressure, enhancing their overall experience. These advancements significantly improve balance, grip control, and walking efficiency.
Despite the progress, AI-powered prosthetics face challenges such as high costs, complex calibration, and the need for continuous learning models. Additionally, ensuring seamless integration with the human nervous system is still an ongoing area of research. However, as AI technology advances, future prosthetic limbs will become more affordable, efficient, and capable of restoring near-natural movement. Innovations like brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and 3D-printed AI prosthetics will further enhance accessibility and improve the lives of millions worldwide.
Comments