5G in IoT & Smart Cities
1. what is 5G in IoT & Smart Cities?

5G in IoT & Smart Citiesplays a transformative role by providing the high-speed, low-latency connectivity required to support the massive networks of devices and systems that make up these environments. With its enhanced bandwidth, ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (mMTC), 5G is the foundation for enabling smart cities and expanding IoT ecosystems in ways that were not possible with previous network generations.
In IoT, 5G enables the connection of millions to billions of devices, each requiring different communication capabilities. The high-speed, high-capacity characteristics of 5G make it ideal for connecting smart devices like sensors, wearables, smart home appliances, and vehicles, as it provides quick and reliable data transmission. 5G's massive machine-type communication (mMTC) allows for the simultaneous connection of a large number of low-power devices, essential for industries like agriculture, healthcare, and logistics. For example, smart factories can use 5G to connect sensors and machines in real-time, allowing for improved automation, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource management.
n Smart Cities, 5G supports infrastructure that enhances urban living by improving public services, reducing energy consumption, and increasing overall efficiency. Smart traffic management systems, for example, use 5G to collect and analyze real-time data from sensors, cameras, and connected vehicles to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance safety. 5G-enabled smart grids allow cities to optimize energy distribution and manage renewable energy sources more effectively. Additionally, smart lighting systems that adjust based on pedestrian movement or daylight can use 5G to communicate with a central system for better energy efficiency.
2.IoT Connectivity via 5G
IoT Connectivity via 5G
revolutionizes the way Internet of Things (IoT) devices communicate, offering enhanced speed, ultra-low latency, and improved reliability. 5G provides the ideal network infrastructure to support the massive scale and diverse needs of IoT applications across industries like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, agriculture, and smart homes. With 5G's high bandwidth, low latency, and massive machine-type communication (mMTC) capabilities, it enables seamless, real-time communication between billions of devices, making the IoT ecosystem more efficient and scalable.
One of the key features of 5G IoT connectivity is its ability to handle massive numbers of connected devices. 5G supports mMTC, which can handle millions of low-power devices transmitting small amounts of data over long periods. This is essential for smart cities, smart homes, and agriculture, where numerous sensors and devices need to be connected to gather real-time data. For example, in smart farming, sensors placed in fields can transmit data about soil moisture levels, crop health, and weather conditions, allowing for more precise irrigation and crop management. The low power consumption of 5G devices ensures that they can operate for extended periods without frequent recharging, making it ideal for IoT applications that require long-range connectivity and low operational costs.
Moreover, 5G IoT connectivity enables ultra-reliable, low-latency communication (URLLC) that is critical for time-sensitive IoT applications. For instance, in autonomous vehicles, IoT devices need to communicate with each other and with road infrastructure in real-time to ensure safe and efficient operation. The low latency of 5G ensures that data can be transmitted almost instantaneously, preventing accidents and optimizing traffic management. Similarly, remote surgery and robotics applications require real-time control and feedback between IoT devices and central systems. In smart factories, robots, machines, and sensors can communicate instantly to adjust production lines, predict maintenance needs, and optimize workflows. 5G makes these applications possible by reducing the time it takes for devices to exchange critical data, enabling near-instantaneous decision-making and response.

3.Smart Traffic Management
Smart Traffic Management
powered by 5G and IoT technologies is transforming the way cities manage traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve road safety. In traditional traffic management systems, data is collected from traffic lights, sensors, and cameras, but the processing of this data is often slow and inefficient. With 5G connectivity, real-time data from IoT sensors and connected vehicles can be analyzed almost instantly, allowing for more efficient traffic control and decision-making. This enables dynamic traffic signal control, real-time updates to drivers, and predictive analytics to improve the overall traffic management system.
A key benefit of 5G-powered smart traffic systems is the ability to optimize traffic flow in real-time. For example, smart traffic lights equipped with sensors can communicate with each other, adjusting their timings based on current traffic conditions. If one intersection experiences heavy congestion, the signal times can be adjusted dynamically to allow more cars to pass through, reducing overall traffic build-up. Similarly, connected vehicles can share their location, speed, and other data with nearby vehicles and infrastructure, enabling better coordination between vehicles and road systems. This results in more efficient routes, fewer accidents, and less time spent in traffic.
Additionally, 5G-based smart traffic management systems can enhance public safety by incorporating real-time monitoring of road conditions, accidents, and emergency situations. In the event of an accident or road hazard, IoT devices such as cameras and sensors can instantly detect the problem and send alerts to drivers via their in-car navigation systems or smartphone apps. Emergency responders can be alerted immediately, and traffic signals can be adjusted to prioritize the movement of emergency vehicles. Predictive analytics can also help in identifying traffic hotspots or areas prone to accidents, allowing city planners to make data-driven decisions for infrastructure development and urban planning. In the long term, smart traffic management systems will create safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly cities by reducing fuel consumption, minimizing congestion, and lowering carbon emissions.

Smart Traffic Management
powered by 5G and IoT technologies is transforming the way cities manage traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve road safety. In traditional traffic management systems, data is collected from traffic lights, sensors, and cameras, but the processing of this data is often slow and inefficient. With 5G connectivity, real-time data from IoT sensors and connected vehicles can be analyzed almost instantly, allowing for more efficient traffic control and decision-making. This enables dynamic traffic signal control, real-time updates to drivers, and predictive analytics to improve the overall traffic management system.
A key benefit of 5G-powered smart traffic systems is the ability to optimize traffic flow in real-time. For example, smart traffic lights equipped with sensors can communicate with each other, adjusting their timings based on current traffic conditions. If one intersection experiences heavy congestion, the signal times can be adjusted dynamically to allow more cars to pass through, reducing overall traffic build-up. Similarly, connected vehicles can share their location, speed, and other data with nearby vehicles and infrastructure, enabling better coordination between vehicles and road systems. This results in more efficient routes, fewer accidents, and less time spent in traffic.
Additionally, 5G-based smart traffic management systems can enhance public safety by incorporating real-time monitoring of road conditions, accidents, and emergency situations. In the event of an accident or road hazard, IoT devices such as cameras and sensors can instantly detect the problem and send alerts to drivers via their in-car navigation systems or smartphone apps. Emergency responders can be alerted immediately, and traffic signals can be adjusted to prioritize the movement of emergency vehicles. Predictive analytics can also help in identifying traffic hotspots or areas prone to accidents, allowing city planners to make data-driven decisions for infrastructure development and urban planning. In the long term, smart traffic management systems will create safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly cities by reducing fuel consumption, minimizing congestion, and lowering carbon emissions.

4.5G for Smart Agriculture
5G for Smart Agriculture
is a game-changer, transforming the way farming is done by introducing advanced technologies that improve efficiency, reduce costs, and boost productivity. With 5G's ultra-fast connectivity, low latency, and ability to handle massive numbers of devices, farmers can implement IoT devices such as sensors, drones, and cameras in their fields to collect real-time data on soil conditions, crop health, weather, and irrigation systems. This data can then be analyzed quickly, enabling farmers to make more informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, pest control, and harvest timing, ultimately leading to better yield and resource optimization.
One of the key advantages of 5G in smart agriculture is the ability to support real-time, large-scale data collection and analysis. Sensors embedded in the soil can monitor moisture levels, pH, and temperature, while drones can capture high-resolution images of crops and analyze their health through computer vision. With 5G’s low latency, this data can be transmitted almost instantaneously to cloud platforms where machine learning algorithms process it and provide actionable insights. For example, precision irrigation systems can adjust water levels automatically based on the real-time moisture content of the soil, reducing water waste and improving crop yield. Autonomous tractors and harvesting machines can also communicate in real-time with each other and the central system, optimizing the farming process.
Additionally, 5G networks enable the integration of AI and machine learning in agriculture, allowing for predictive analytics to forecast crop diseases, pest infestations, and potential yield outcomes. By collecting and analyzing data from multiple sensors and environmental factors, farmers can take preventive actions before issues become widespread, reducing the need for pesticides and fertilizers, and promoting sustainable farming practices. 5G's high bandwidth also supports high-definition video feeds from cameras placed in the field or on drones, enabling remote monitoring and inspection, which can be especially beneficial in large-scale farming operations. In smart agriculture, 5G allows farmers to harness the full potential of connected devices, making agriculture more efficient, profitable, and sustainable in the long run.

5.Remote Healthcare via 5G
Remote Healthcare via 5G
is revolutionizing the way healthcare services are delivered, enabling patients to receive high-quality care regardless of their location. 5G technology, with its ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and ability to connect a vast number of devices simultaneously, is the key enabler of telemedicine and remote monitoring. In traditional healthcare systems, distance can be a significant barrier, particularly for individuals in rural or underserved areas. With 5G, doctors and healthcare professionals can remotely monitor patients in real-time, offering immediate consultations, diagnoses, and treatment recommendations without the need for in-person visits. This is particularly important for individuals with chronic conditions who need constant monitoring, as 5G can transmit patient data quickly and efficiently, allowing for timely interventions.
The real-time capabilities of 5G can also enhance remote surgeries and virtual consultations by providing seamless, low-latency video connections that allow specialists to perform or assist in procedures remotely. Surgeons can operate robotic systems from distant locations with minimal delay, ensuring precision even in complex procedures. 5G’s high bandwidth allows for the transmission of high-definition video, ensuring clear communication during consultations and surgeries. Additionally, wearable devices connected through 5G can track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, transmitting this data to healthcare professionals in real-time. This helps in continuous patient monitoring, enabling early detection of health issues and reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
Beyond individual care, 5G-enabled remote healthcare also supports healthcare facilities in providing more effective and coordinated care. Smart hospitals equipped with 5G technology can enable instant access to patient records, diagnostic results, and real-time communication between medical teams, improving patient care coordination. 5G networks allow the use of AI-powered diagnostic tools, remote imaging, and robotic assistance, which makes healthcare more accurate and efficient. As 5G infrastructure continues to expand, the accessibility and affordability of remote healthcare will increase, making it possible for people worldwide to access top-tier medical services from the comfort of their homes, significantly improving global health outcomes.

6.5G-powered Autonomous Vehicles
5G-powered Autonomous Vehicles
represent a significant leap forward in the development of self-driving cars, trucks, and other vehicles. 5G technology, with its ultra-low latency, high-speed connectivity, and massive device support, is essential for enabling the safe, efficient, and seamless operation of autonomous vehicles. One of the core challenges for self-driving vehicles is their need to process vast amounts of real-time data from a variety of sensors, cameras, and other connected devices. 5G's high bandwidth enables the rapid transmission of this data, allowing autonomous vehicles to react to their environment almost instantaneously. This is crucial for handling dynamic traffic conditions, detecting obstacles, and communicating with other vehicles and infrastructure in real-time, improving both safety and efficiency.
In 5G-powered autonomous vehicles, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication plays a critical role. This technology allows vehicles to communicate not only with each other but also with infrastructure, such as traffic lights, road signs, and pedestrians, as well as with cloud-based systems. With 5G's low latency, vehicles can make split-second decisions based on real-time data shared between vehicles and surrounding infrastructure. For instance, a self-driving car can receive information about road conditions, traffic signal changes, or even an accident ahead from other vehicles, allowing it to adjust its route or speed without any delay. This V2X communication enhances the ability of autonomous vehicles to operate in complex environments, leading to smoother traffic flow, reduced congestion, and fewer accidents.
Additionally, 5G-powered autonomous vehicles are essential for the widespread adoption of smart cities. In these urban environments, vehicles will not only communicate with each other but also with various city-wide networks to optimize transportation systems. This includes efficient route planning, managing traffic signals, and coordinating with public transportation systems. 5G’s capabilities enable these vehicles to interact with centralized cloud-based platforms that manage and analyze data from thousands of vehicles, providing real-time updates and insights. The result is a safer, more efficient, and sustainable transportation system where vehicles are better coordinated, leading to reduced traffic jams, lower emissions, and improved mobility overall. With 5G, the dream of fully autonomous, interconnected vehicles becomes a tangible reality, paving the way for future smart mobility solutions.
7.5G for Industrial IoT
5G for Industrial IoT
is transforming industries by enabling faster, more reliable, and scalable connections for a wide range of smart devices and systems. In industrial environments, IIoT refers to the use of sensors, machines, and connected devices to collect, analyze, and act on data in real time. However, traditional wireless networks often struggle with the high data volumes, low latency, and reliability required for industrial applications. 5G technology, with its high-speed, low-latency capabilities, is perfectly suited to address these challenges, allowing for more efficient operations, predictive maintenance, and improved safety in industrial settings.
One of the key advantages of 5G in IIoT is its ability to support massive device connectivity. Industrial operations often involve thousands or even millions of devices, sensors, and machines that need to be connected simultaneously. 5G's massive machine-type communication (mMTC) allows industries to scale their operations without worrying about network congestion. This means that factories, warehouses, and supply chains can have real-time data from a multitude of devices, helping to improve process control, optimize production lines, and enable smarter decision-making. Additionally, 5G’s ultra-low latency ensures that devices can communicate instantly, allowing for real-time monitoring and quick responses to changing conditions in industrial settings. This is especially crucial in high-speed manufacturing, where delays in communication can lead to costly downtime and errors.
Another significant impact of 5G on IIoT is its role in enabling predictive maintenance and improving operational efficiency. With 5G's fast data transfer, machines and equipment can be continuously monitored in real-time. Sensors embedded in industrial equipment can detect early signs of wear and tear, vibrations, temperature changes, or other anomalies. The data collected is then transmitted via 5G networks to central systems or cloud platforms for analysis. Predictive analytics algorithms can process this data to forecast when equipment is likely to fail, allowing companies to perform maintenance before breakdowns occur, thus reducing unplanned downtime and repair costs. Moreover, the combination of 5G and AI-powered analytics can optimize workflows, streamline production processes, and enhance safety by allowing for immediate responses to hazardous situations or emergencies.

8.Smart Energy Grids
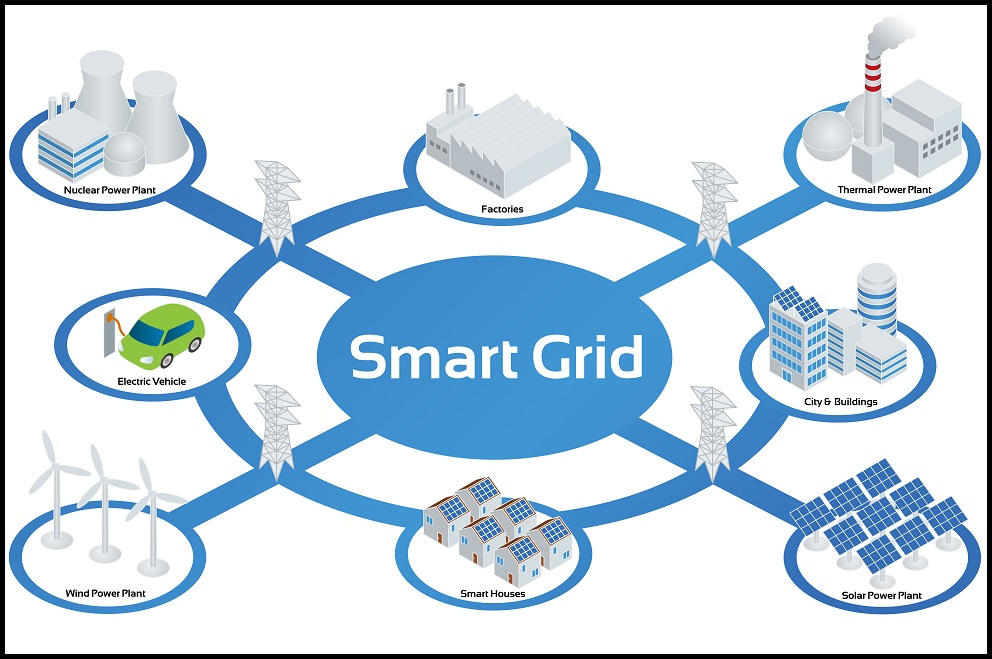
Smart Energy Gridsare an advanced version of traditional power grids that use digital technology and advanced communication networks to manage the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity more efficiently and sustainably. Unlike conventional grids, which are largely one-way systems, smart grids enable bidirectional communication between utilities and consumers, creating a more interactive and responsive energy system. The key advantage of a smart grid is its ability to integrate renewable energy sources (such as solar, wind, and hydro) more effectively, as well as to support advanced energy storage solutions. This is critical in the transition to clean energy, as it helps accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation and ensures a stable, reliable supply of power.
One of the core components of smart energy grids is the use of sensors, meters, and advanced analytics to continuously monitor the grid’s health and performance in real-time. These technologies enable utilities to collect detailed data on energy usage patterns, detect faults, and make adjustments remotely. For example, smart meters provide real-time readings of electricity consumption at the consumer level, allowing users to monitor their energy usage and make more informed decisions about reducing waste or optimizing consumption. Utilities can also use this data to forecast demand more accurately, improve load balancing, and reduce the likelihood of outages. Additionally, smart grids support dynamic pricing, where electricity rates can fluctuate based on demand, incentivizing consumers to reduce consumption during peak hours, leading to a more balanced energy system.
Another important feature of smart energy grids is their ability to optimize energy distribution and improve grid resilience. By using advanced control systems and predictive algorithms, smart grids can automatically reroute power during outages or prevent blackouts by balancing supply and demand across different areas. This improves the reliability of the grid and ensures that power is distributed more equitably across urban, suburban, and rural areas. The integration of renewable energy sources and distributed energy resources (DERs), such as home solar panels, battery storage, and electric vehicles, also helps reduce dependence on centralized power generation, making the grid more sustainable and decentralized. Moreover, smart energy grids play a crucial role in achieving carbon reduction goals by facilitating the integration of clean energy technologies, improving energy efficiency, and enabling energy management at the individual consumer level, all of which help create a more sustainable and low-carbon energy ecosystem.
Smart Energy Gridsare an advanced version of traditional power grids that use digital technology and advanced communication networks to manage the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity more efficiently and sustainably. Unlike conventional grids, which are largely one-way systems, smart grids enable bidirectional communication between utilities and consumers, creating a more interactive and responsive energy system. The key advantage of a smart grid is its ability to integrate renewable energy sources (such as solar, wind, and hydro) more effectively, as well as to support advanced energy storage solutions. This is critical in the transition to clean energy, as it helps accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation and ensures a stable, reliable supply of power.
One of the core components of smart energy grids is the use of sensors, meters, and advanced analytics to continuously monitor the grid’s health and performance in real-time. These technologies enable utilities to collect detailed data on energy usage patterns, detect faults, and make adjustments remotely. For example, smart meters provide real-time readings of electricity consumption at the consumer level, allowing users to monitor their energy usage and make more informed decisions about reducing waste or optimizing consumption. Utilities can also use this data to forecast demand more accurately, improve load balancing, and reduce the likelihood of outages. Additionally, smart grids support dynamic pricing, where electricity rates can fluctuate based on demand, incentivizing consumers to reduce consumption during peak hours, leading to a more balanced energy system.
Another important feature of smart energy grids is their ability to optimize energy distribution and improve grid resilience. By using advanced control systems and predictive algorithms, smart grids can automatically reroute power during outages or prevent blackouts by balancing supply and demand across different areas. This improves the reliability of the grid and ensures that power is distributed more equitably across urban, suburban, and rural areas. The integration of renewable energy sources and distributed energy resources (DERs), such as home solar panels, battery storage, and electric vehicles, also helps reduce dependence on centralized power generation, making the grid more sustainable and decentralized. Moreover, smart energy grids play a crucial role in achieving carbon reduction goals by facilitating the integration of clean energy technologies, improving energy efficiency, and enabling energy management at the individual consumer level, all of which help create a more sustainable and low-carbon energy ecosystem.

Comments