5G Technology
5G technology is the fifth-generation wireless network that offers ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and higher connectivity for advanced applications like IoT, AI, and smart cities.
5G technology is the fifth-generation wireless network that offers ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and higher connectivity for advanced applications like IoT, AI, and smart cities.
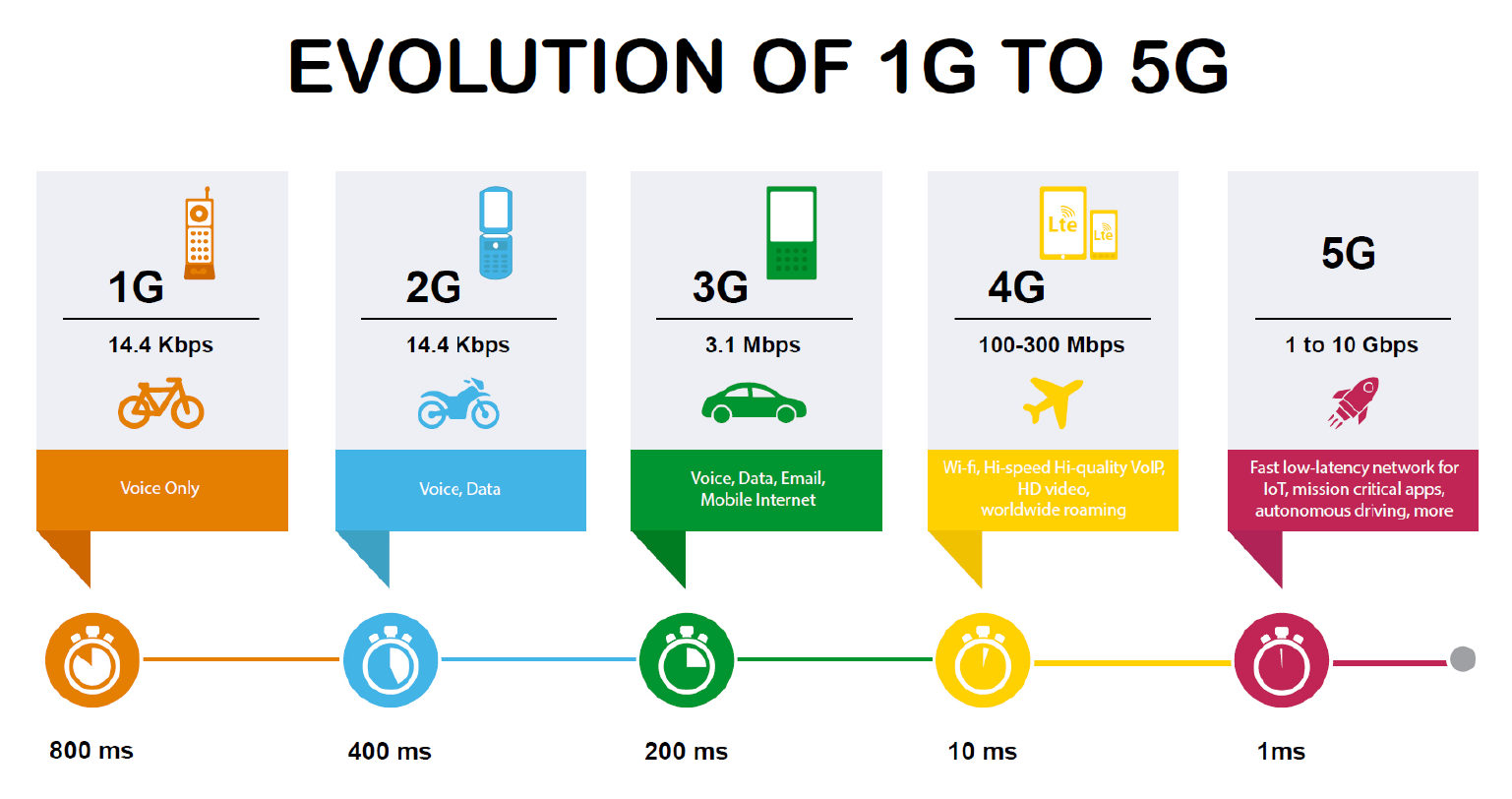
The evolution of wireless technology has dramatically transformed communication, with each generation introducing significant improvements over its predecessor. 5G (Fifth Generation) is the latest advancement, offering enhanced speed, lower latency, and greater connectivity compared to previous generations like 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G. 1G, introduced in the 1980s, was the first mobile network, enabling analog voice communication but with poor sound quality and no security. 2G brought digital voice calls, SMS (text messaging), and basic encryption, making mobile communication more secure and efficient. The arrival of 3G enabled mobile internet access, video calls, and multimedia messaging, significantly improving connectivity. With 4G LTE, data speeds increased drastically, allowing for high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and faster browsing.
5G surpasses 4G in multiple ways, including speed, latency, and network capacity. While 4G networks offer speeds of up to 1 Gbps, 5G can deliver speeds of 10 Gbps or more, making downloads and streaming almost instantaneous. The latency (network response time) in 4G is around 30-50 milliseconds, whereas 5G reduces it to as low as 1 millisecond, enabling real-time applications like autonomous driving, remote surgery, and smart city operations. Additionally, 5G supports massive device connectivity, allowing more IoT (Internet of Things) devices to be linked without network congestion. This is crucial for smart homes, industrial automation, and large-scale communication systems, which require seamless data exchange between thousands of devices.
Another major difference is network efficiency and spectrum usage. 4G primarily uses lower frequency bands (below 6 GHz), which provide decent coverage but can get congested in crowded areas. In contrast, 5G operates across multiple bands, including millimeter waves (mmWave) in the 24-100 GHz range, offering ultra-fast speeds but requiring more infrastructure, such as small cell towers. Additionally, beamforming and network slicing technologies make 5G more efficient by dynamically allocating resources based on demand. While 5G is still being deployed worldwide, its capabilities will revolutionize industries, enabling advancements in AI-driven automation, edge computing, and immersive AR/VR experiences, setting the stage for a more connected future.
Click here for more information
The 5G infrastructure is the foundation of next-generation wireless communication, designed to support ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and massive device connectivity. Unlike previous generations, 5G does not rely solely on large cellular towers but instead incorporates a mix of advanced technologies to ensure seamless and efficient network coverage. The core components of 5G infrastructure include small cell networks, massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) antennas, fiber-optic backhaul, and network slicing. Small cell networks, consisting of low-power base stations, are deployed in urban areas to improve coverage and handle high data traffic. These cells enhance signal strength and ensure uninterrupted connectivity, especially in densely populated cities. Massive MIMO antennas use multiple antennas on both transmission and reception ends, increasing network capacity and improving data throughput.
Another critical aspect of 5G infrastructure is the fiber-optic backhaul, which connects small cells and base stations to the internet. Unlike traditional backhaul methods, fiber-optic cables offer high-speed data transmission with minimal latency. Additionally, network slicing enables operators to create virtual networks within the 5G infrastructure, allowing customized connectivity solutions for different industries. For instance, autonomous vehicles require ultra-low latency for real-time decision-making, while smart factories may prioritize high-bandwidth connections for automation. Through network slicing, 5G can cater to these diverse needs efficiently.
5G infrastructure also includes edge computing, which processes data closer to the source rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making applications like real-time AI, augmented reality (AR), and remote healthcare more effective. Furthermore, 5G networks leverage millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum, providing higher frequencies for faster speeds but requiring more base stations to ensure coverage. Despite challenges like higher deployment costs and infrastructure upgrades, 5G infrastructure is revolutionizing industries, enabling innovations in smart cities, connected vehicles, and industrial automation, setting the stage for the future of communication.
Click here for more information

The integration of 5G with the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing smart cities by enabling ultra-fast, low-latency, and highly reliable connectivity for billions of devices. Unlike previous networks, 5G offers massive machine-type communication (mMTC), which allows a vast number of IoT devices to communicate seamlessly. Smart city applications like intelligent traffic management, smart street lighting, environmental monitoring, and connected healthcare rely on real-time data exchange, which 5G efficiently supports. With speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G and ultra-low latency of 1 millisecond, 5G enables instantaneous data processing for critical IoT applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote medical surgeries
Smart cities leverage 5G to enhance urban infrastructure and improve citizens' quality of life. One key application is smart traffic systems, where 5G-enabled sensors and AI-driven analytics help optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and prevent accidents by providing real-time updates. Additionally, smart grids and energy management systems benefit from 5G by enabling precise monitoring and control of power distribution, renewable energy sources, and efficient electricity consumption. Public safety is also enhanced through 5G-powered surveillance systems, which use AI-driven facial recognition and real-time analytics to detect security threats instantly. Furthermore, 5G in disaster management allows authorities to deploy drones, sensors, and AI models to assess damage and provide immediate assistance.
The future of 5G-powered smart cities looks promising, with innovations in autonomous transportation, remote healthcare, and AI-driven city planning. As 5G networks expand, smart cities will witness advancements in connected vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, allowing self-driving cars to interact with infrastructure and pedestrians safely. In healthcare, 5G-enabled IoT medical devices will enable remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and AI-assisted diagnostics. However, challenges such as cybersecurity threats, high infrastructure costs, and regulatory policies must be addressed to ensure the safe and widespread adoption of 5G in IoT and smart cities. By implementing robust security frameworks, AI-driven network monitoring, and strategic public-private partnerships, 5G will continue to transform cities into more sustainable, efficient, and intelligent urban environments................
Click here for more information

With the rapid adoption of 5G technology, security and privacy concerns have become a major focus. Unlike previous generations, 5G networks rely on virtualized infrastructure, software-defined networking (SDN), and a vast number of connected devices, making them more vulnerable to cyber threats. One of the key security challenges in 5G is the increased attack surface due to the deployment of small cells, edge computing, and massive IoT (Internet of Things) devices. Cybercriminals can exploit these points to launch attacks such as DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service), data interception, and malware injection. Additionally, 5G’s reliance on cloud-based architectures raises concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access. Ensuring end-to-end encryption, robust authentication mechanisms, and secure network slicing is essential to protect users and organizations.
Privacy risks in 5G networks are another critical issue. As 5G enables more real-time data collection from millions of devices, personal information, location tracking, and usage patterns become more vulnerable. Network slicing, while beneficial for customized services, can also introduce privacy loopholes if not properly secured. Malicious actors can attempt to gain access to sensitive user data through intercepting communication channels or exploiting weak authentication protocols. Moreover, governments and telecom providers must ensure that 5G surveillance mechanisms are transparent and do not infringe on individual privacy rights. Implementing privacy-preserving technologies such as anonymization, encryption, and secure multi-party computation (SMPC) can help mitigate these risks.
To strengthen 5G security and privacy, organizations and governments are implementing advanced cybersecurity measures such as AI-powered threat detection, zero-trust architecture, and quantum-resistant encryption. AI-driven security systems can monitor network traffic in real-time to detect anomalies and prevent cyberattacks before they escalate. Zero-trust security models ensure that every user, device, and application is continuously authenticated, reducing the chances of unauthorized access. Additionally, as quantum computing advances, post-quantum cryptography is being explored to future-proof 5G networks. By integrating these cutting-edge security frameworks, 5G networks can become more resilient, ensuring safe and private communication for users, businesses, and governments worldwide...............
Click here for more information

The future of 5G extends far beyond just high-speed internet and low latency. As 5G adoption increases globally, industries will witness revolutionary advancements in automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT). The rollout of 5G-Advanced (5.5G) is expected to enhance network efficiency, improve energy consumption, and provide even lower latency for real-time applications. Future networks will support massive machine-type communication (mMTC) and ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), enabling seamless integration of autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and smart city applications. With speeds reaching 10 Gbps and beyond, the next phase of 5G will unlock innovations in remote surgeries, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and metaverse applications, making digital interactions more immersive than ever.
Beyond 5G, the emergence of 6G technology is expected to redefine connectivity with terahertz (THz) frequencies, AI-driven network optimization, and quantum communication. 6G aims to provide holographic communication, extreme energy efficiency, and ultra-high-speed wireless networks with data rates up to 100 times faster than 5G. Innovations such as brain-computer interfaces (BCI), AI-powered network automation, and satellite-based internet will become mainstream, enabling seamless global connectivity, real-time digital twins, and intelligent automation. Additionally, space-based 6G networks will help bridge the digital divide by providing high-speed internet access in remote and underserved regions, ensuring universal connectivity.
The transition to 5G and beyond also presents challenges such as cybersecurity risks, privacy concerns, and infrastructure costs. Governments and tech companies are actively working on AI-driven cybersecurity frameworks, blockchain-based network security, and sustainable energy solutions to ensure secure and eco-friendly deployment of next-gen networks. The integration of edge computing, quantum cryptography, and self-optimizing networks will further enhance network reliability and data protection. As 6G research accelerates, we can expect intelligent, hyper-connected, and AI-driven ecosystems that will redefine industries, reshape human interactions, and create a truly interconnected digital world.
.........
Click here for more information

Comments